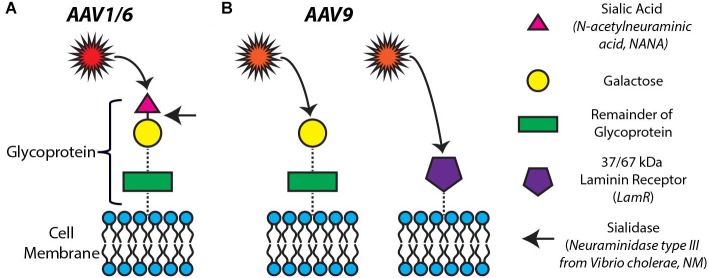
FIGURE 3.
Proposed mechanisms of infectivity for AAV1, 6, and 9. (A) Cell surface N-linked sialic acid has been proposed as the primary receptor for AAV1 and 6 to infect and transduce cells. The removal of sialic acid by neuraminidase (targeting the portion of the glycoprotein indicated by the arrow) is expected to block the AAV1,6-mediated transduction of cells. (B) AAV9-mediated cell infection/transduction has been attributed to two receptors: terminal galactose on cell surface glycoproteins (left panel) and the 37/67 kDa laminin receptor (LamR) (right panel).