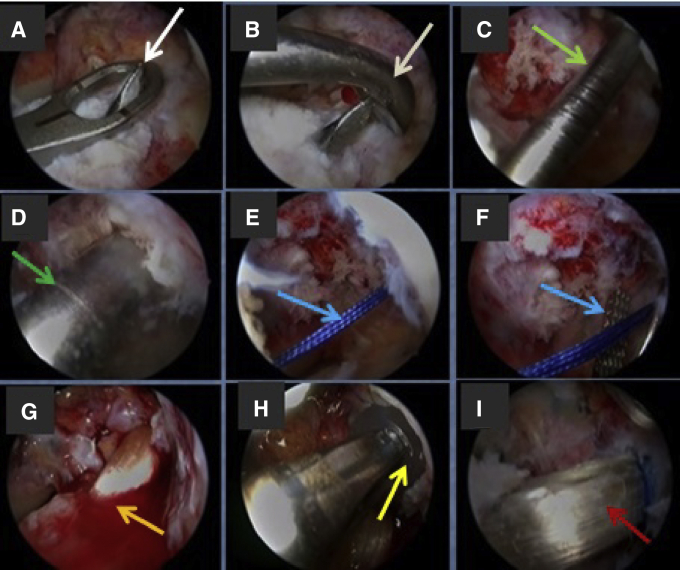
Fig 5.
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction. Arthroscopic view through lateral portal in a left knee. (A) The ACL guidewire (white arrow) is drilled. (B) A curette over the pin (white arrow) is used during reaming for protection. (C) The ACL guide pin (green arrow) is drilled in the femoral footprint. (D) The femoral tunnel is reamed by an appropriately sized reamer (green arrow). (E) Passing sutures (blue arrow) are passed through the femoral tunnel using the guidewire. (F) The passing sutures in the femoral tunnel are kept there and retrieved (blue arrow) through the ACL tibial tunnel. (G) The ACL graft (orange arrow) is passed through the tibial tunnel to the joint and then to the femoral tunnel. (H) The ACL graft is fixed at the femoral tunnel by an interference screw (yellow arrow). (I) ACL graft (red arrow) after complete fixation.