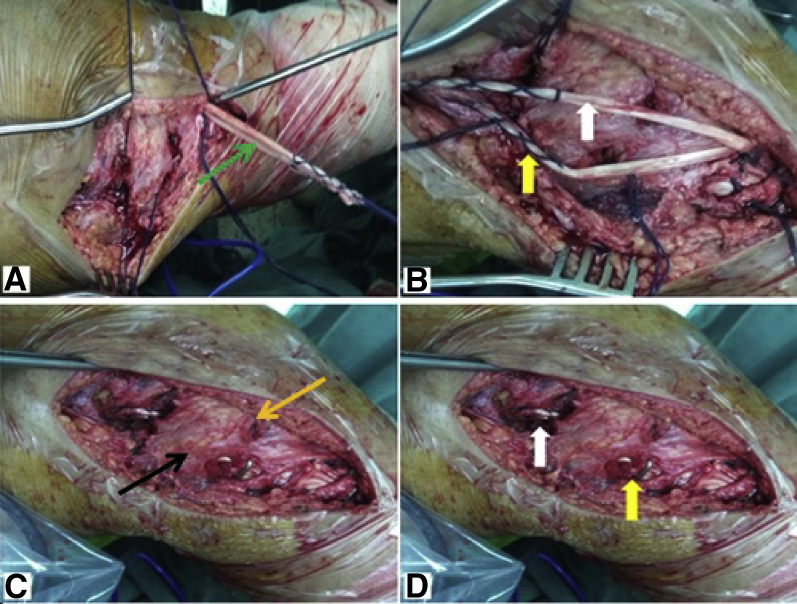
Fig 6.
Open medial collateral ligament–posterior oblique ligament reconstruction of left knee (with patient supine and knee flexed 30° during graft fixation). (A) The 2 limbs of the gracilis (green arrow) are suspended on the anterior cruciate ligament graft at the distal end of the tibial tunnel and fixed. (B) The anterior limb of the gracilis (white arrow) is used for medial collateral ligament reconstruction, and the posterior limb (yellow arrow) is used for posterior oblique ligament reconstruction. (C) The anterior limb of the gracilis is passed through the anterior subfascial tunnel (orange arrow), and the posterior limb of the gracilis is passed through the posterior subfascial tunnel (black arrow). (D) The posterior limb of the gracilis is fixed by a metal staple (yellow arrow) at point D, and both limbs are fixed by an interference screw (white arrow) at point F.