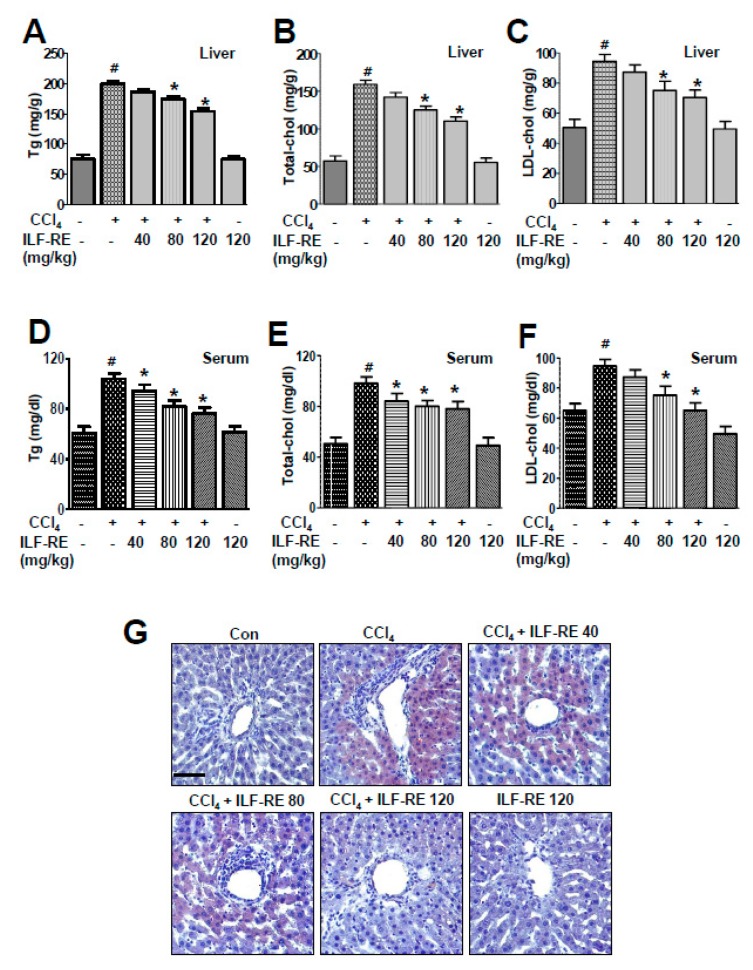
Figure 8.
ILF-RE regulates hepatic lipid accumulation in CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity. Rats were intraperitoneally treated with CCl4 (0.2 mL/100 g, BW) twice a day for 4 weeks. ILF-RE (40, 80, or 120 mg/kg) was co-administered with CCl4 or 120 mg/kg ILF-RE on its own for 4 weeks, followed by harvesting of the liver and serum. Liver triglycerides (A), liver total-cholesterol (B), liver LDL-cholesterol (C), serum triglyceride (D), serum total-cholesterol (E), and serum LDL-cholesterol (F) were examined. Representative images of the liver sections from each group stained with Oil Red O for lipid content (G). Scale bars = 50 µM. The experiments were performed in triplicate using tissues from at least three rats in each group. # p < 0.05 vs. Con group; * p < 0.05 vs. CCl4 group (n = 10 rats per group). BW, body weight; Con, control; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; ILF-RE, the combination R. verniciflua with E. ulmoides.