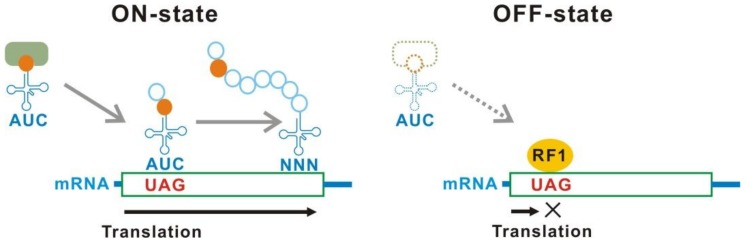
Figure 1.
Translational switch using a UAG read-through in Escherichia coli. In the ON-state, an aminoacyl-tRNACUA incorporates the amino acid at an inserted UAG in a target mRNA, resulting in a stop codon read-through and full-length translation of the target gene products. On the other hand, when the aminoacyl-tRNACUA is not supplied in the OFF-state, the UAG is solely recognized as a stop codon and the synthesis of full-length products is interrupted by the peptide release factor 1. Circles and boxes indicate amino acids and protein coding regions in mRNAs, respectively. aaRS, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. tRNACUA, UAG suppressor tRNA. RF1, peptide release factor 1.