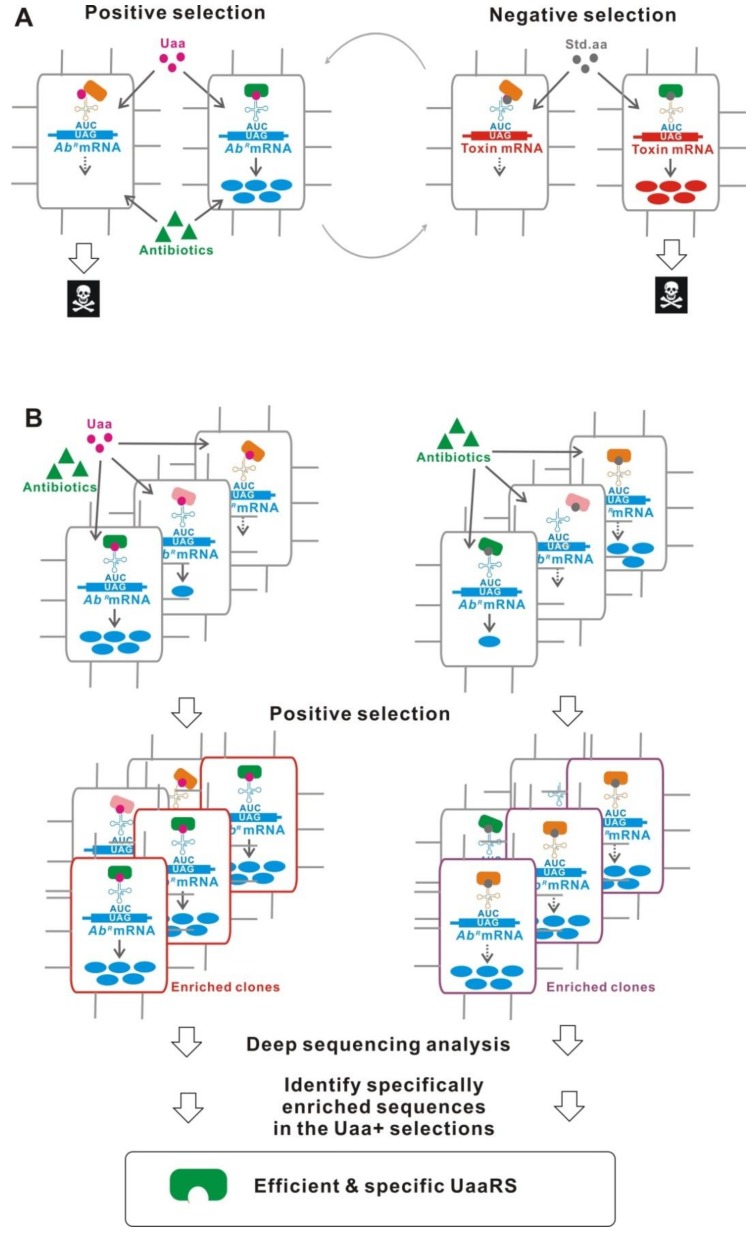
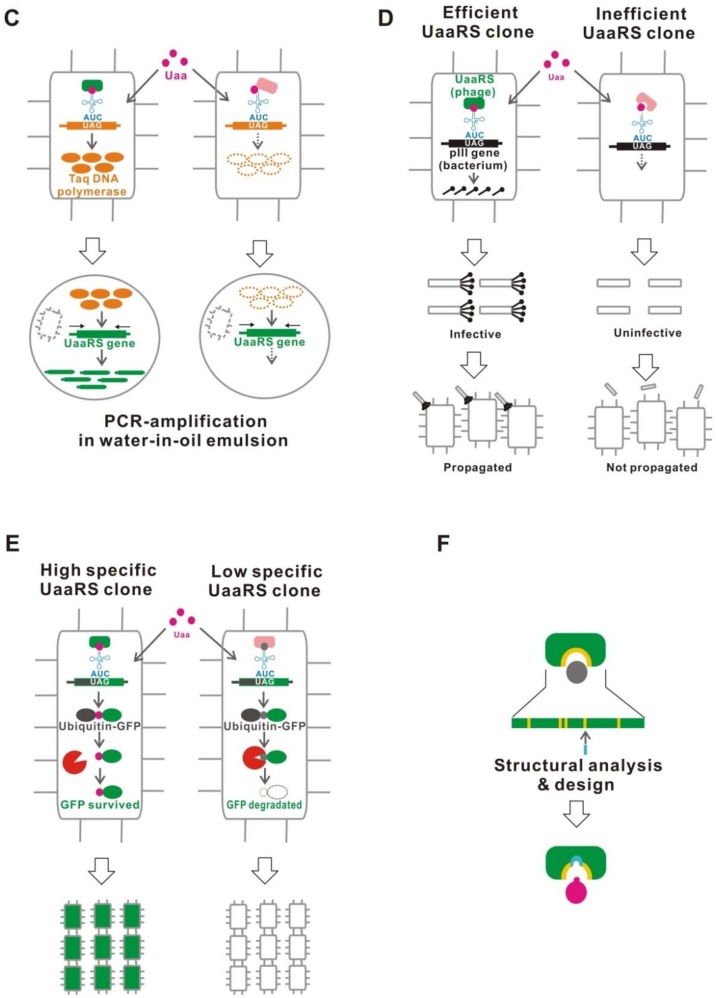
Figure 7.
Improvement of UaaRS/tRNACUA. (A) Traditional evolution method. A positive selection and a negative selection are performed to effectively isolate the Uaa incorporating and less Std. aa incorporating UaaRSs, respectively. (B) Parallel positive selections combined with deep sequencing and statistical analysis. Positive selections are performed in the presence and absence of Uaa. Specifically-enriched sequences in the Uaa selection, which encode efficient and specific UaaRSs, are identified after deep sequencing. (C) Compartmentalized partnered replication. DNA sequences that encode highly active UaaRSs are selectively amplified in compartmentalized micro-drops. (D) Phage-assisted continuous evolution. Phage carrying a highly active UaaRS are selectively propagated. (E) Post-translational proofreading. The proteins containing certain desired N-terminal Uaas have longer half-lives. Genes encoding highly specific UaaRSs are identified in bacteria expressing high amounts of GFP. The bacteria can then be isolated using a cell sorter. (F) Molecular design based on structural data.