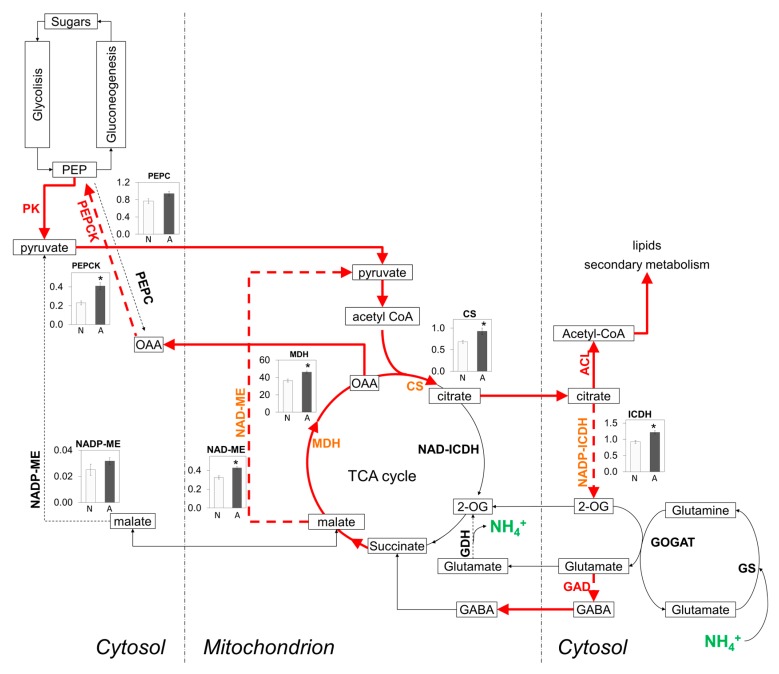
Figure 3.
C anaplerotic routes (dotted arrows) in ammonium-fed roots of A. thaliana plants. Ammonium (NH4+) release or incorporation to metabolic pathways is highlighted in green bold text. Induced routes and proteins with higher abundance in ammonium relative to nitrate nutrition are highlighted in red (bold lines and text). Increased activity of anaplerotic and TCA-cycle enzymes are shown in orange bold text and emphasized with an asterisk (*) in the activity graphs. Graphs represent enzyme activity of Arabidopsis roots fed with ammonium (grey bars) or with nitrate (white bars). Enzyme activities are expressed as: CS (nmol CoA mg−1 FW min−1); ICDH (nmol NADP mg−1 FW min−1); MDH (nmol NADP mg−1 FW min−1); NAD-ME (nmol NAD mg−1 FW min−1); NADP-ME (nmol NADP mg−1 FW min−1); PEPC (nmol NADH mg−1 FW min−1); PEPCK (nmol NADH mg−1 FW min−1). Data shown in graphics represent mean values ± SE (n = 4). Asterisk (*) indicates significant N source effect (t-test, p < 0.05). Abbreviations: ATP-citrate lyase (ACL); citrate synthase (CS); gamma-amniobutyric acid (GABA). glutamate decarboxylase (GAD); glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH); glutamate synthase (GOGAT); glutamine synthetase (GS); NAD-isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD-ICDH); NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP-ICDH); malate dehydrogenase (MDH); NADP-malic enzyme (NADP-ME); NAD-malic enzyme (NAD-ME); phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP); phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC); phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK); pyruvate kinase (PK).