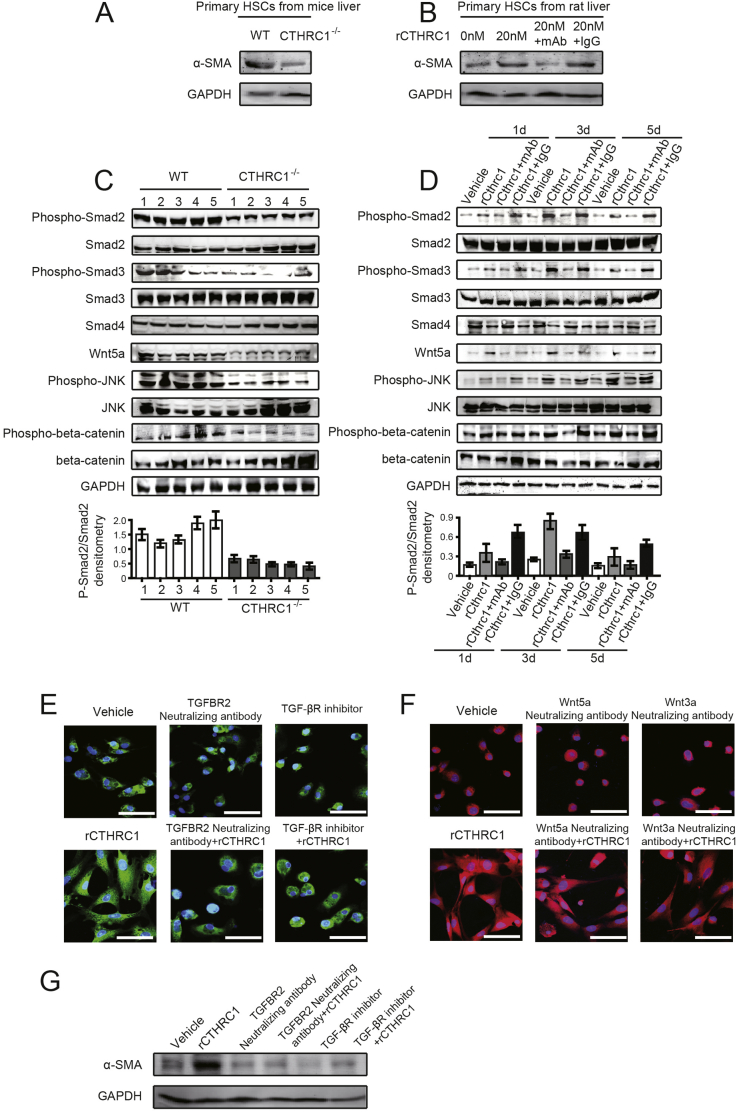
Fig. 4.
CTHRC1 activates both TGF-β and Wnt signaling, while the promotive effect of CTHRC1 on HSC activation is mainly dependent on TGF-β signaling.
A. The expression of α-SMA in primary HSCs after 7 days isolated from WT and CTHRC1−/− mice.
B. The expression of α-SMA in primary rat HSCs after 4 days, which were treated with vehicle, 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein alone, and 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein plus CTHRC1 mAb or IgG.
C. Western blotting analysis of phosphorylation of Smad2, Smad3, JNK, total Smad4 and expression of Wnt5a in five liver tissues of WT or CTHRC1−/− mice intraperitoneally injected with CCl4. GAPDH was the loading control. The densitometry of p-Smad2/Smad2 was shown below.
D. Phosphorylation of Smad2, Smad3, JNK, total Smad4 and expression of Wnt5a in primary rat HSCs, which were treated with vehicle, 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein, and 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein plus CTHRC1 mAb or IgG for 1, 3, 5 days, individually. GAPDH was the loading control. The densitometry of p-Smad2/Smad2 was shown below.
E and F. Representative immunofluorescence images of α-SMA (green in E, red in F) in primary rat HSCs after 4 days, which were treated with vehicle, 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein, and 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein plus neutralizing antibodies or inhibitor as follows: TGFBR2 neutralizing antibody or TGF-β receptor inhibitor (E), Wnt5a or Wnt3a neutralizing antibody (F). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 μm.
G. The expression of α-SMA in primary rat HSCs after 4 days, which were treated with vehicle, 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein, and 20 nM rCTHRC1 protein plus TGFBR2 neutralizing antibody or TGF-β receptor inhibitor. GAPDH was the loading control. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)