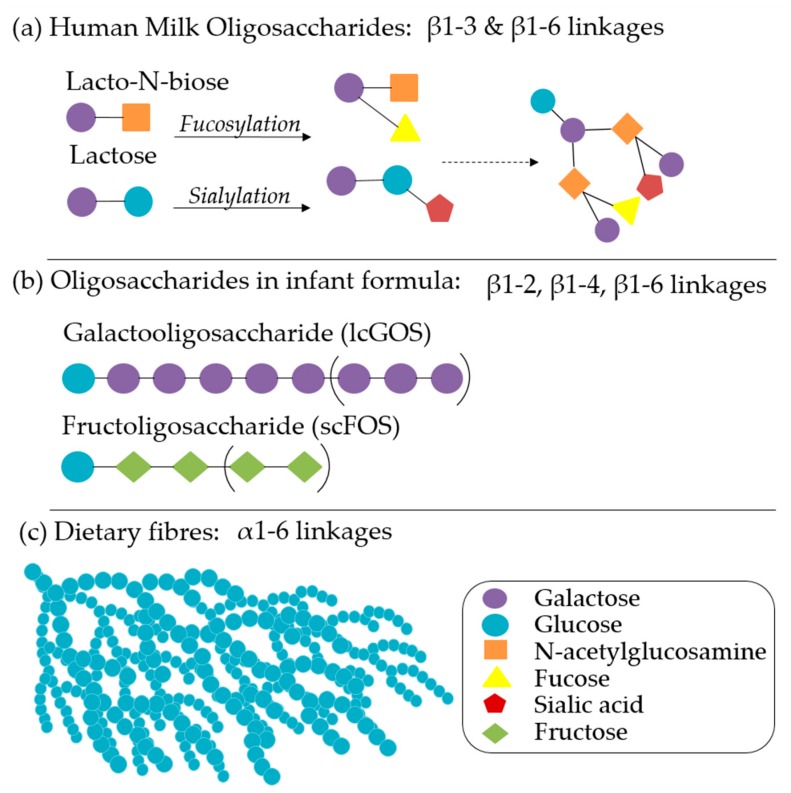
Figure 2.
(a) The core structures of human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), common modification pathways, and an example of a complex HMO, connected by β1-3 and β 1-6 linkages that are resistant to enzymatic cleavage by human-derived enzymes. (b) The structure of galactooligosaccharide (long chain) and fructooligosaccharide (short chain), which are common prebiotic molecules in supplemented infant formulas: β1-2, β1-4, and β1-6 linkages are resistant to enzymatic cleavage by human derived enzymes. (c) A model of dietary starch, characterized by glucose molecules connected by α1-6 linkages in a complex higher structure, which contributes to incomplete enzymatic cleavage by human enzymes.