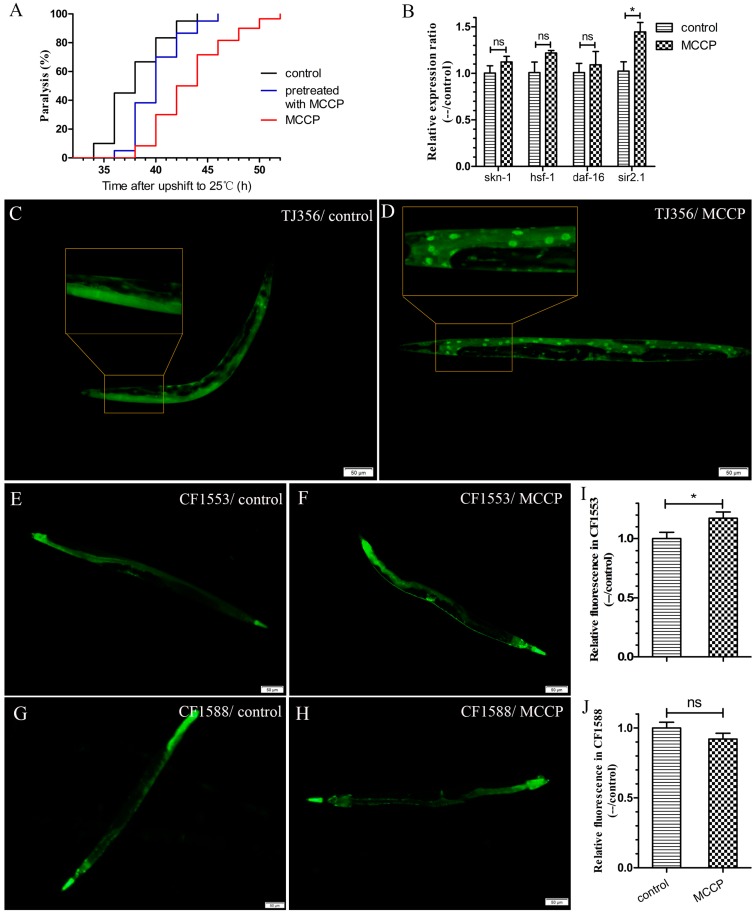
Figure 3.
MCCP exposure upregulated the sir-2.1 transcript level and promoted the DAF-16 nuclear translocation. (A) CL4176 worms were incubated at 16 °C for 48 h on agar media dishes containing MCCP, either moved to control dishes or maintained on MCCP dishes, and then induced to express Aβ1–42. It was indicated that obvious protection against paralysis was observed even in worms shifted to control dishes before induction of Aβ1–42 expression. Mean ± SD for control, pretreatment with MCCP and MCCP were 38.00 ± 2.73, 40.10 ± 2.45 and 43.43 ± 3.67 respectively (control with pretreatment with MCCP and MCCP, p < 0.001). (B) The transcript levels of sir-2.1, hsf-1, daf-16, and skn-1 in CL4176 worms treated with and without MCCP were quantified using qRT-PCR. The data was obtained from three independent experiments. (C,D) MCCP treatment was able to accelerate nuclear localization of DAF-16::GFP in C. elegans (TJ356). Data was obtained from three independent experiments (10 worms each). (E,H) The expression of SOD-3 in SOD-3::GFP worms (CF1553 and CF1588) treated with or without MCCP. Data was obtained from three independent experiments (10 worms each). (I,J) The fluorescence intensity from SOD-3::GFP in day-4-adults was calculated by Image pro plus. Comparisons between treatments and controls were significant, * p < 0.05. Data were obtained from three independent experiments (10 worms in each group). (ns meant that the difference was not significant).