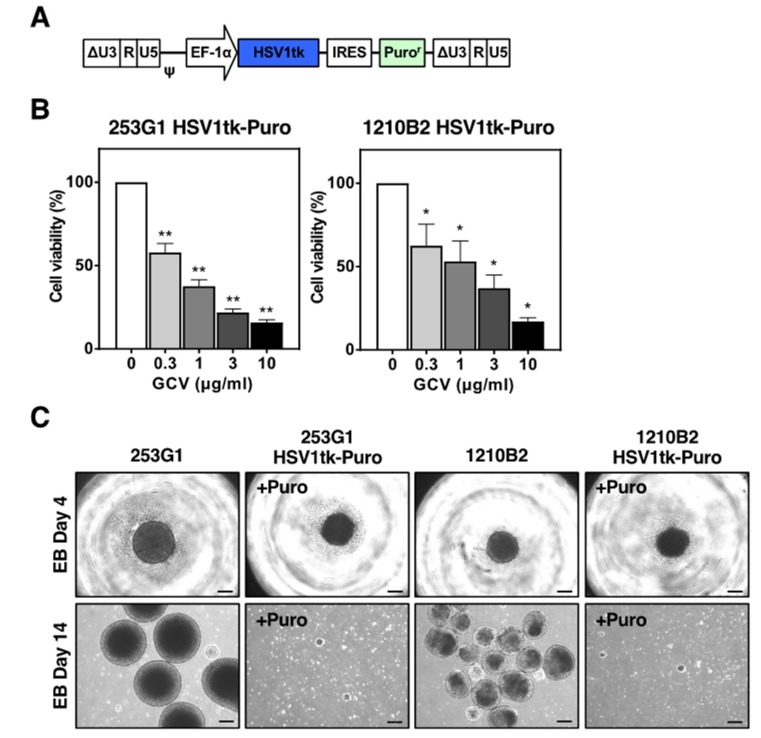
Figure 1.
Transduction of human iPSCs with the lentiviral vector expressing the HSV-TK gene. (A) Schematic representation of the integrated proviral form of the lentiviral vector expressing the HSV1tk gene. HSV1tk, humanized-codons with CpG-free HSV-TK gene; EF-1α, human elongation factor 1 α subunit promoter; IRES, internal ribosomal entry site; Puror, puromycin resistance gene; ΔU3, deletion of enhancer/promoter in the U3 region of the LTR; ψ, packaging signal. (B) Puromycin-resistant 253G1 and 1210B2 iPSCs transduced with the lentiviral vector expressing the HSV1tk gene were cultured in the presence of various concentrations of GCV for 2–5 days. Cell viability was assessed by the CCK-8 assay. The percent cell viability was calculated relative to cells in the absence of GCV. There was no significant difference in the results obtained on days 2, 3, 4, and 5 of culture. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 4–5). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. (C) Representative images of EB formation of 253G1, 1210B2, 253G1 HSV1tk-Puro, and 1210B2 HSV1tk-Puro iPSCs on day 4 and day 14. 253G1 HSV1tk-Puro and 1210B2 HSV1tk-Puro iPSCs were cultured with 1 μg/mL puromycin (+Puro). Scale bar, 200μm.