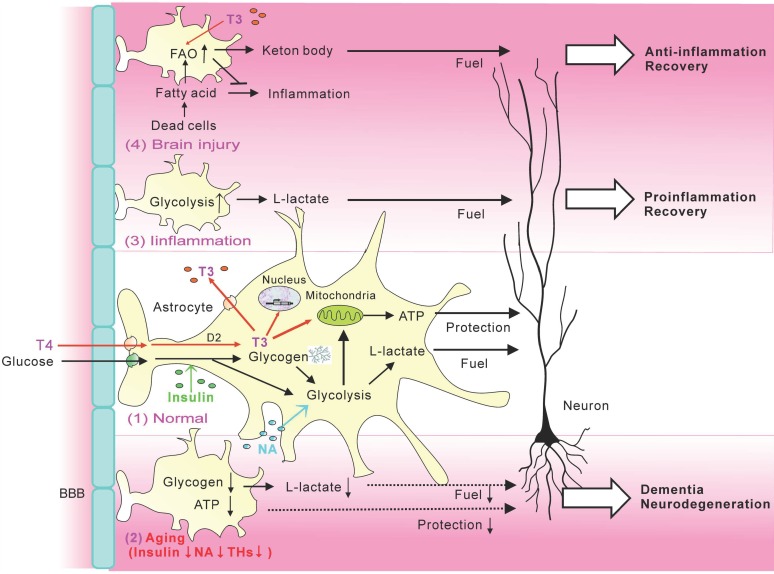
Figure 1.
Metabolic plasticity of astrocytes. (1) In normal astrocytes, insulin upregulates glucose uptake from blood stream, NA-stimulated glycolysis, and T4 is converted to T3 and upregulated ATP production in mitochondria. Astrocytic L-lactate fuels neurons, while neuroprotective functions of astrocytes are maintained by ATP production. (2) The reductions of insulin, NA, and THs with aging downregulate astrocytic fuel provision and protection of neurons. (3) Astrocytic glycolysis is upregulated after inflammation, resulting in the increase of fuel for neurons, as well as proinflammatory reactive astrocytes. (4) Astrocytic FAO is upregulated after FAO and further accelerated by T3, resulting in the clearance of inflammatory fatty acid derived from dead cells, as well as the production of ketone bodies for fueling neurons.