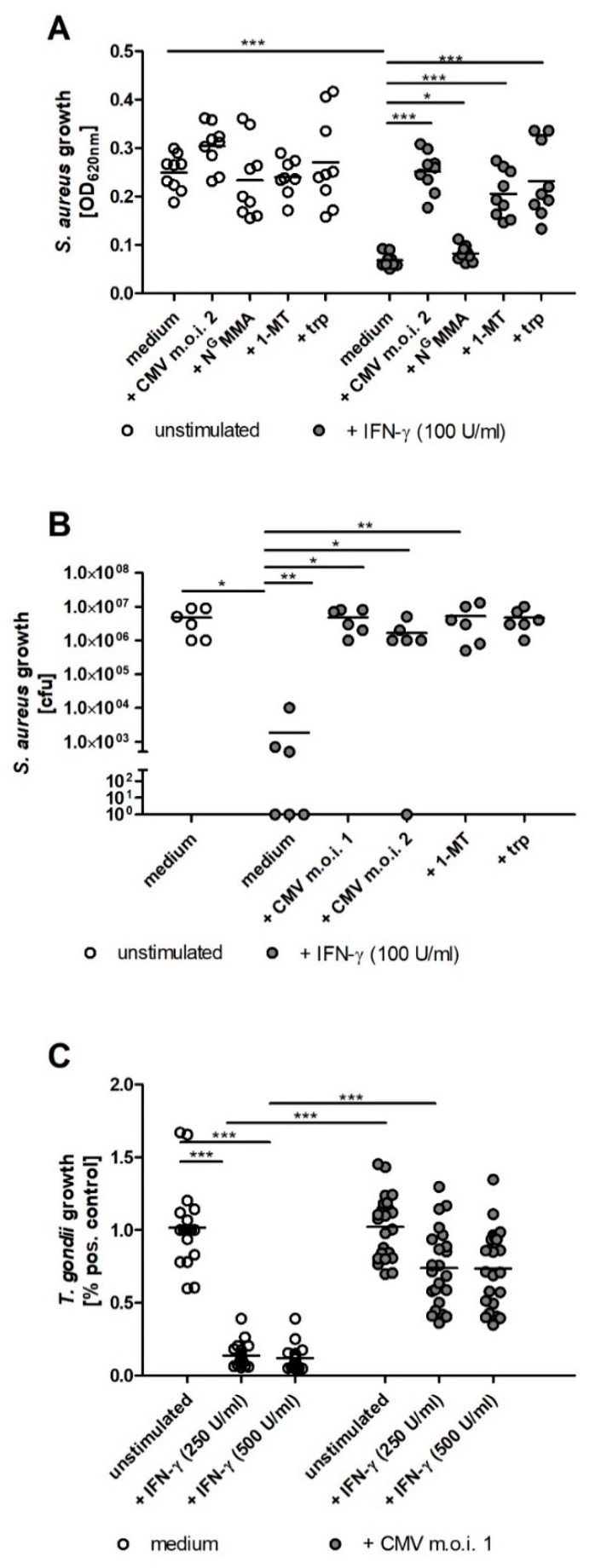
Figure 2.
IDO1-mediated antibacterial and antiparasitic effects are lost in hRPE cells upon CMV infection. 3 × 104 hRPE cells were stimulated in 96-well plates with indicated amounts of human IFN-γ (0 to 500 U/mL) in the presence of CMV (m.o.i. 1 or 2), NGMMA (100 µg/mL), 1-methyl-tryptophan (1-MT; 1.5 mM), or l-tryptophan (trp; 100 µg/mL). After 72 h the cell culture supernatants were harvested and infected with Staphylococcus aureus (10–100 cfu/well) (A,B) or Toxoplasma gondii (3 × 104 ME49 tachyzoites per well) (C). S. aureus growth was detected by measurement of the optical density at 620 nm after 16 h (A) or by counting the colony forming units (cfu; B). T. gondii growth was measured after three days using the 3H-uracil incorporation method. Data are given as mean ± SEM of three (A,B) or eight (C) experiments, each performed in triplicate. Significant differences to the unstimulated or uninfected group were marked with asterisks (n.s. = not significant; * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.001 and *** p ≤ 0.0001). The nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test was used.