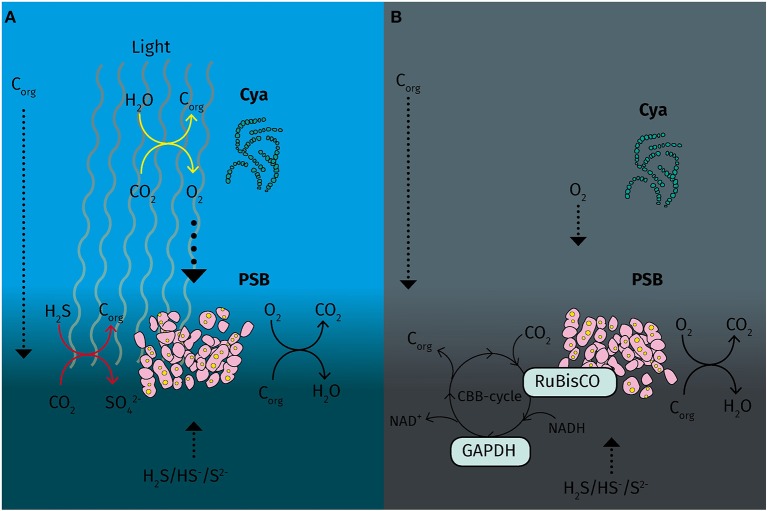
Figure 5.
Schematic overview of carbon fixation and energy metabolism of “Thiodictyon syntrophicum” strain Cad16T during day and night under micro oxic conditions in the Lake Cadagno chemocline. (A) During the day cyanobacteria spp. locally produce oxygen that potentially is used by PSB strain Cad16T for respiration. In parallel, strain Cad16T is actively oxidizing sulfide and fixing inorganic carbon in anoxygenic photosynthesis. (B) At night, low levels of oxygen remain in the chemocline and are used as electron acceptor in substrate respiration in strain Cad16T. The RuBisCO form II is possibly active in maintain the redox balance using CO2 as an electron acceptor. Corg, organic carbon; Cya, cyanobacteria; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde−3-dehydrogenase; PSB, purple sulfur bacteria; RuBisCO, ribulose−1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Dotted arrows, diffusive processes; Yellow arrows, oxygenic photosynthesis; red arrows, anoxygenic photosynthesis; black arrows, chemotrophic reactions.