Figure 5.
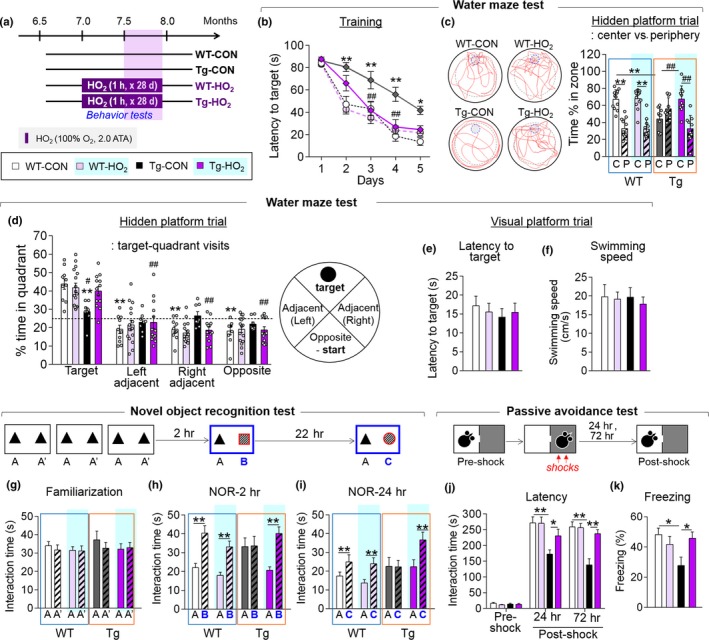
HO2 improved the cognitive deficits of Tg‐APP/PS1 mice. (a) Experimental design. Mice were treated with HO2 (100% O2, 2 ATA) from 7 months of age for 1 hr daily for 28 days. Behavioral tests were performed in this order: water maze test (WM), novel object recognition test (NOR), and passive avoidance test (PA). The color codes in the legends are applicable to all parts of Figure 5. (b) The latency to finding the hidden platform during the training in the water maze test for WT‐CON, WT‐HO2, Tg‐CON, and Tg‐HO2. (c and d) Representative tracking in the hidden platform trial. The percent time spent in the periphery vs. the center (c) and in each quadrant. Representative tracking of each group (d). Dashed line on (d) indicates a 25% chance of finding the platform. C, center; P, periphery; T, target; L, left; R, right; O, opposite. (e and f) The latency to finding the platform (e) and swim speed (f) during the visual platform trial of WT‐CON, WT‐HO2, Tg‐CON, and Tg‐HO2. (g–i) The effects of HO2 on novel object recognition memory. Time spent exploring between the two identical objects during the familiarization (g), and between a new and an old object 2 hr after familiarization (h, NOR‐2h) and 24 hr after familiarization (i, NOR‐24h). (j and k) The effects of HO2 on fear memory in the PA. The latency to entering the dark chamber at the preshock, and 24 and 72 hr after shock (j), and the freezing time 24 hr after shock (k). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. WT‐CON, n = 7–18; WT‐HO2, n = 8–18; Tg‐CON, n = 7–12; Tg‐HO2, n = 8–14 per each group. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, difference between indicated groups; # p < 0.05; ## p < 0.01, difference between Tg‐CON and Tg‐HO2 (two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test and two‐way repeated‐measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test)
