Fig. 1.
The core TFs identified in the liver.
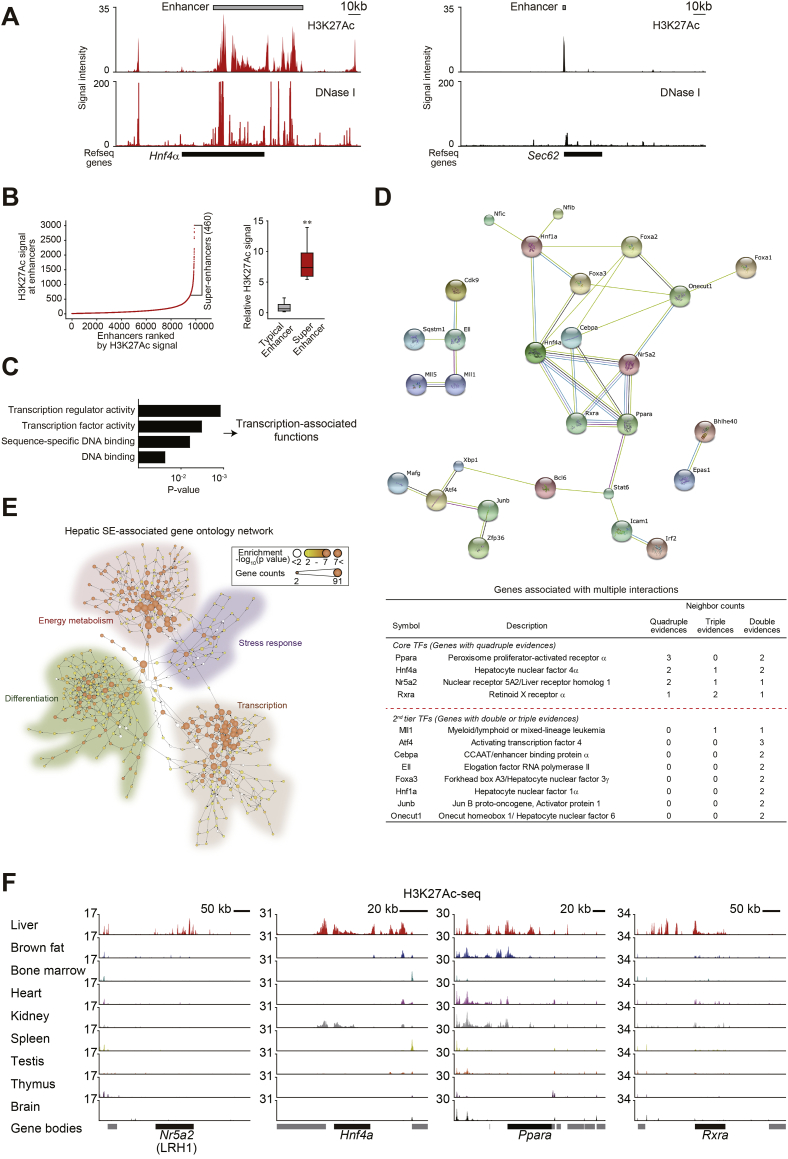
(A) H3K27Ac ChIP-seq and DNase-seq profiles at the Hnf4a (left) and the Sec62 (right) loci in mouse liver. Gray bars indicate enhancer regions.
(B) Distribution of H3K27Ac ChIP-seq signal intensities across 9891 enhancers in the liver. H3K27Ac occupancy was not evenly distributed across the enhancer regions, with a subset of 460 enhancers containing exceptionally high amounts of H3K27Ac (i.e., super-enhancers) (left). A box plot of H3K27Ac ChIP-seq densities at constituent enhancers within 9431 typical enhancers or 460 super-enhancers (right).
(C) Gene ontology (GO) functional categories regarding molecular functions for super-enhancer-associated genes. Genes encoding for the factors controlling transcription were enriched.
(D) A protein-protein interaction network of super-enhancer-associated transcription factors (TFs) according to STRING database. LRH1 (also known as Nr5a2), HNF4α, PPARα, and RXRα make a core network. The TFs were divided into two groups (multiple interactions with quadruple evidences and multiple interactions with double or triple evidences) according to the number of evidences in the above network. The red dotted line designates the cutoff dividing core and second-tier TFs.
(E) A network displaying interactions between GO categories. Each node indicates GO term. The thickness of node colour represents the degree of statistical significance for enrichment. Node sizes show the number of gene counts assigned to each GO term. The network was generated by analysis of Cytoscape plugin BiNGO.
(F) H3K27Ac ChIP-seq data at the loci of Nr5a2 (LRH1), Hnf4a, Ppara, and Rxra. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)