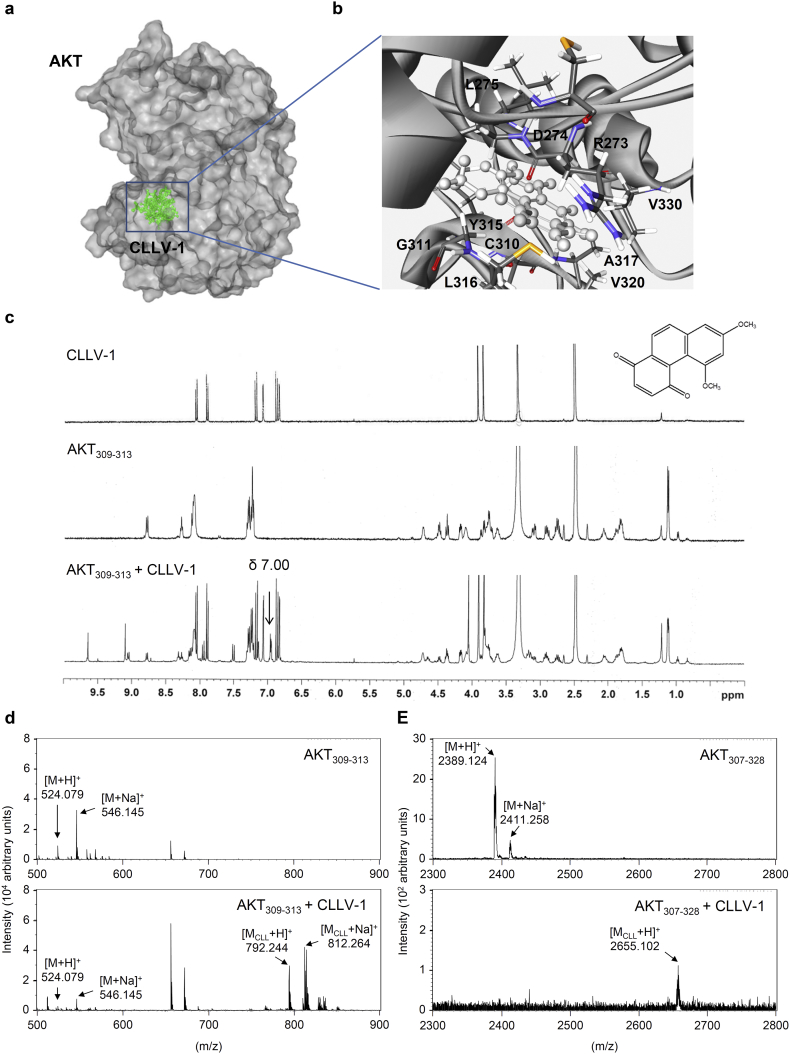
Fig. 6.
CLLV-1 covalently reacts with the thiol group of an AKT cysteine in vitro. (a-b) Docking models of CLLV-1-targeted AKT. Surface presentation demonstrates the structure of AKT (gray). CLLV-1 moieties are colored green and rendered in stick representation (a). Close-up of CLLV-1 docking site (best energy mode) (b). The figures were prepared using Discovery Studio 4.1. The crystal structure of AKT was downloaded from PDB (accession code 4ekl). The chemical structure of CLLV-1 was drawn by ChemDraw Ultra 9.0. (c) 1H NMR spectra of CLLV-1 (upper panel), synthetic AKT peptide (AKT309–313; FCGTP) (middle panel), and mixtures of CLLV-1 and AKT309–313 (lower panel). (d-e) The synthetic AKT peptides AKT309–313 and AKT307–328 (KTFCGTPEYLAPEVLEDNDYGR) were incubated in the presence or absence of CLLV-1. The molecular mass of the synthetic AKT peptides and their CLLV-1 adducts were detected using MALDI-TOF MS. M, molecular mass of AKT peptides; MCLL, molecular mass of adducts of AKT peptides and CLLV-1. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)