Fig. 3.
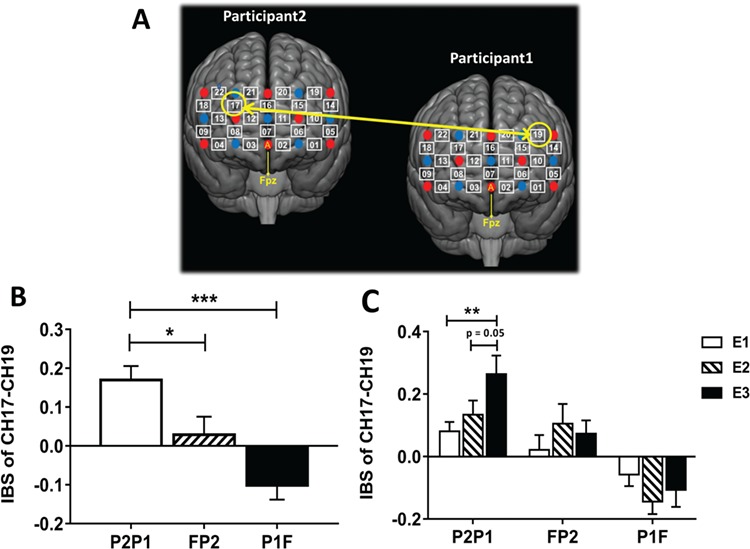
The CH combination showed significant difference in IBS increment among conditions. (A) One-way ANOVA showed a significant main effect of DYAD on the IBS increment of CH17–CH19, which survived the FDR correction (P = 0.05). (B) The amplitude of IBS increment of CH17–CH19. The IBS increment of CH17–CH19 from ‘P2P1’ indicates the IBS increment between the CH17 of ‘P2’ and the CH19 of ‘P1’. The IBS increment of CH17–CH19 from ‘FP2’ indicates the IBS increment between the CH17 of ‘F’ and the CH19 of ‘P2’. The IBS increment of CH17–CH19 from ‘P1F’ indicates the IBS increment between the CH17 of ‘P1’ and the CH19 of ‘F’. (C) The fluctuation of IBS increment of CH17–CH19 from different dyads over time. E1/E2/E3 indicates EPOCH1/EPOCH2/EPOCH3, respectively. The duration of each epoch is 80 s. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
