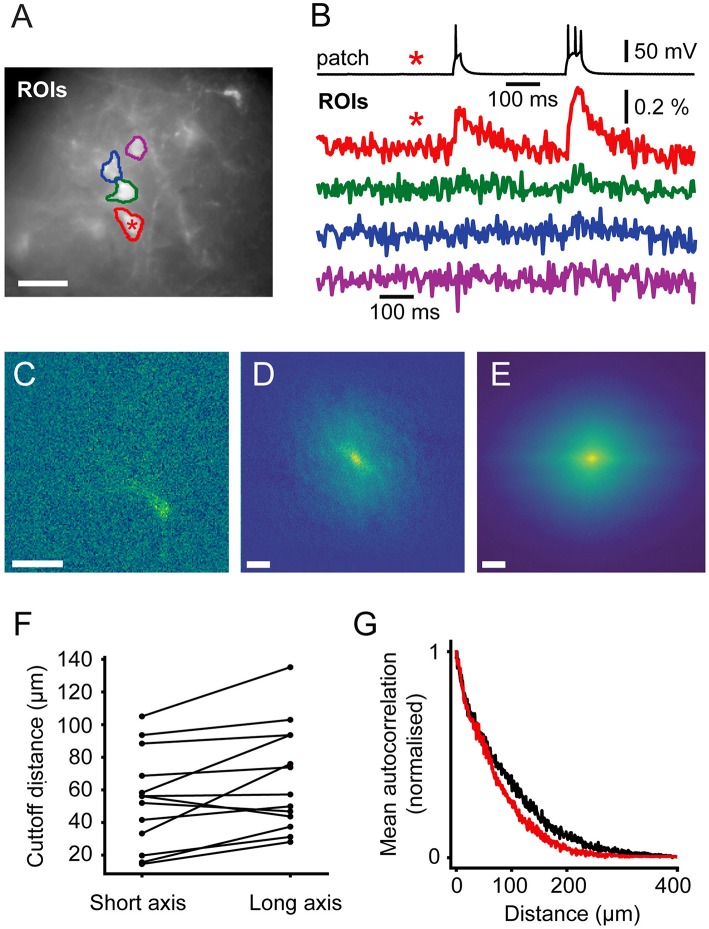
Figure 6.
Signal Spread. Autocorrelation of activity maps can be used to estimate crosstalk. (A) Wide-field image of a patched neuron (red roi) with other neurons in the FOV. (B) Electrophysiological and fluorescent trace from the patched active cell (red and black) and fluorescent traces from ROIs over adjacent cells (green, blue and magenta). A small amount of crosstalk can be seen in the time courses of the adjacent cells. (C) A spatially unfiltered activity map of the same neuron calculated by measuring the sum over frames during the depolarizing stimulus. (D) The 2D spatial autocorrelation of the activity map. This represents the fraction of signal power arising from the patched neuron at different separations. (E) The mean of rotationally aligned autocorrelations of all measured cells. (F) The length of the long and short 50% cut-offs for all cells. (G) The profile of the mean autocorrelation for the long (black) and short (red) axes. Scale bars 40 μm.