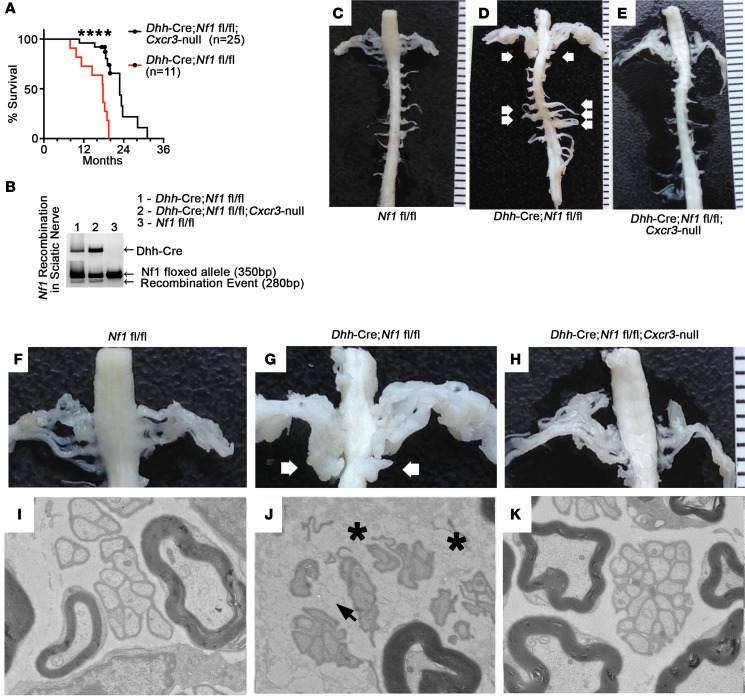
Figure 3. Global deletion of Cxcr3 prevents plexiform neurofibroma and reduces nerve pathology in Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl mice.
(A) Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl Cxcr3-null (n = 25) mice survived significantly longer than Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl (n = 11) mice (****P < 0.0001, log-rank test). All of the Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl and none of the Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl Cxcr3-null mice developed neurofibromas. Censored data points represent Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl Cxcr3-null mice collected at 18 to 20 months of age for dissection, pathological analyses, and histological analyses. (B) Loss of Cxcr3 did not prevent Nf1 recombination in Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl Cxcr3-null sciatic nerve. (C–E) Representative images of age-matched (10-month) spinal cords and associated spinal nerve/DRG are shown; such dissections were performed on all study mice (n > 10 each group). White arrows indicate plexiform neurofibromas. (F–H) Close-up of C–E; white arrows indicate bilateral plexiform neurofibromas compressing the spinal cord. (I–K) Representative electron micrographs from saphenous nerves (n = 3 examined for each genotype). (I) Electron micrograph of a normal 7-month saphenous nerve. (J) Black arrowhead indicates a disrupted Remak bundle in Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl saphenous nerve. Dark gray particulate (black asterisks) indicates deposited collagen. (K) Remak bundle disruption and collagen deposition were absent in 7-month Dhh-Cre Nf1fl/fl Cxcr3-null saphenous nerves. Original magnification, 4000× (I, J, and K).