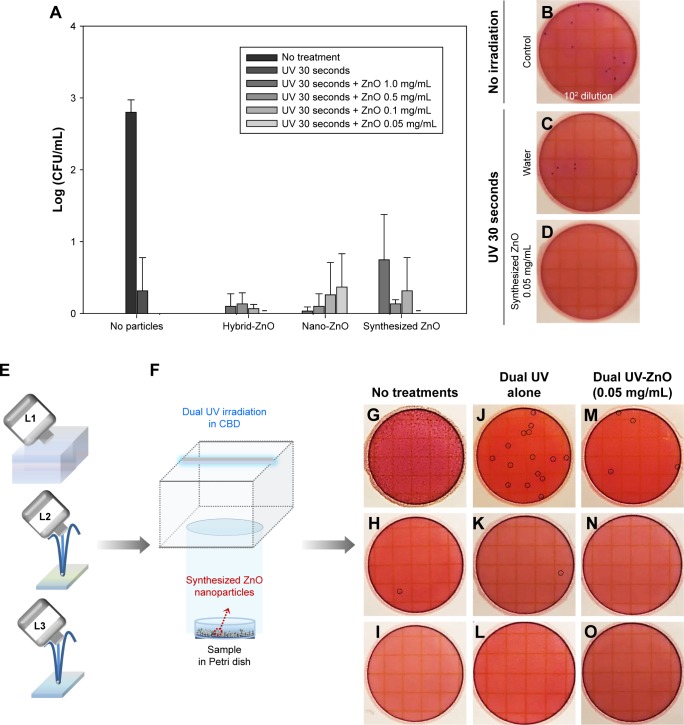
Figure 5.
Antibacterial activity of the dual UV-irradiated ZnO nanoparticles against Escherichia coli.
Notes: (A) Plots of ZnO particle concentration vs log (CFU/mL). Representative plate images of (B) E. coli colonies (102 dilution) with no treatment, (C) E. coli colonies after dual UV irradiation alone (30 seconds), and (D) after dual UV-irradiated (30 seconds)-ZnO nanoparticle (0.05 mg/mL) treatment with a 5-minute incubation period. (E) Schematic diagram of water sampling from L1, L2, and L3 locations (a pool and two fountains) and (F) dual UV irradiation in a CBD with ZnO nanoparticle treatment. (G–O) Representative film images of samples from L1, L2, and L3 treated with/without dual UV-ZnO nanoparticles (G–I, no treatment; J–L dual UV irradiation for 30 seconds; M–O, dual UV [30 seconds]-ZnO nanoparticles [0.05 mg/mL, 5 minutes]). (A) – represents ‘not detected’. (J, M, H, and K) Round dot circles represent E. coli colonies.
Abbreviations: CBD, collimated beam device; UV, ultraviolet; ZnO, zinc oxide.