FIGURE 10.
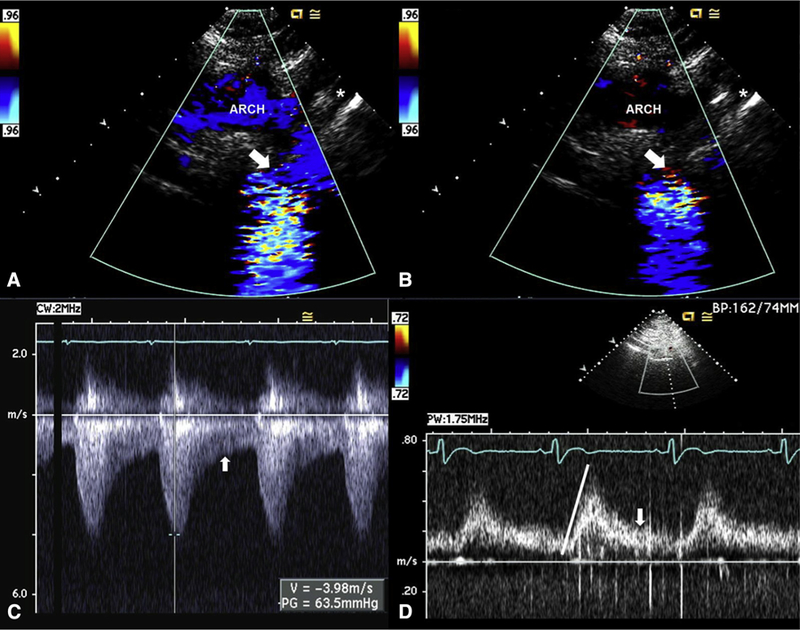
Transthoracic assessment for aortic coarctation. A, Echocardiogram of a 31-year-old woman with BAV and severe aortic coarctation. Suprasternal systolic still frame shows laminar Doppler flow through the proximal portion of the arch (“ARCH”) before becoming turbulent flow across a tight coarctation (arrow) just distal to the left subclavian (asterisk). B, Suprasternal diastolic still frame shows no Doppler flow through the proximal portion of the arch but persistent diastolic turbulent flow across the coarctation (arrow) just distal to the left subclavian (asterisk). C, Continuous-wave Doppler signal across the coarctation shows a systolic (measurement) peak gradient of 64 mm Hg through the coarctation, with persistent flow in diastole (arrow). D, Pulsed-wave Doppler signal of the abdominal aorta shows a delayed peaking of the systolic signal (line) with prominent persistent flow in diastole (arrow), pathognomonic of coarctation.
