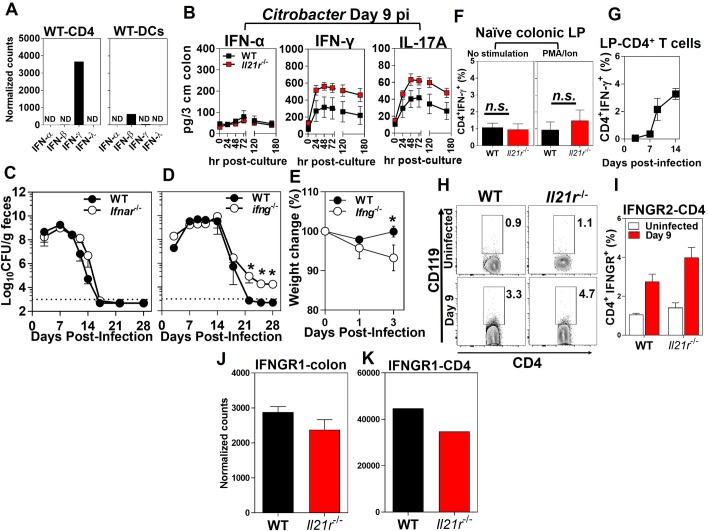
Fig 4. The requirement of IFN-γ, but not IFN-α/β, for the clearance of infection with C. rodentium.
A. The expression levels of interferons (α, β, γ, λ) by the FACS-sorted CD4+ T cells (left) and DCs (right) isolated from the distal colonic LP of WT mice 9 days p.i. Results are from pooled distal colon LP of WT mice (n = 25) 9 days after infection with C. rodentium analyzed by Nanostring. N.D., not detected. B. Cytokine ELISA kinetics of IFN-α, IFN-γ and IL-17A from supernatants of the ex-vivo organ culture of the colonic tissues from WT or Il21r-/- mice collected at 9 days p.i. (sampled at times indicated during the 180 hr cultures). Data are the Mean ± SEM of one experiment from two independent experiments with a total of 10 (Il21r-/-) or 10 (WT) mice/group. C. Bacterial burden in the feces of C. rodentium-infected Ifnar-/- versus WT controls as shown by colony forming units (CFU)/g feces. D. Bacterial infection kinetics in the feces and E. changes in body weight of Ifng-/- mice versus WT controls following infection with C. rodentium. The dashed line represents the sensitivity of the culture method. The results are the Mean ± SEM of 5 mice per group. *p < 0.05 determined by Mann-Whitney U test. F. Intracellular expression of IFN-γ by CD4+- T cell isolated from the distal colon LP of Il21r-/- mice or WT controls with (left panel) or without (right panel) PMA/ionomycin stimulation. G. The kinetics of the intracellular expression of IFN-γ by ovalbumin-specific mucosal CD4+ T cells in WT mice at 3, 7, 9, and 14 days after OVA-C. rodentium infection, as determined by flow cytometry. H-K. The expression of IFN-γR1 and IFN-γR2 (CD119) by CD4+ T cells isolated from the LP of the distal colon of uninfected Il21r-/- and WT mice (n = 7/genotype) and infected mice 9 days p.i. (n = 4/genotype). Data are the Mean ± SEM of percentage of CD119+CD4+ T cells, with statistical significance determined by Mann-Whitney U test.