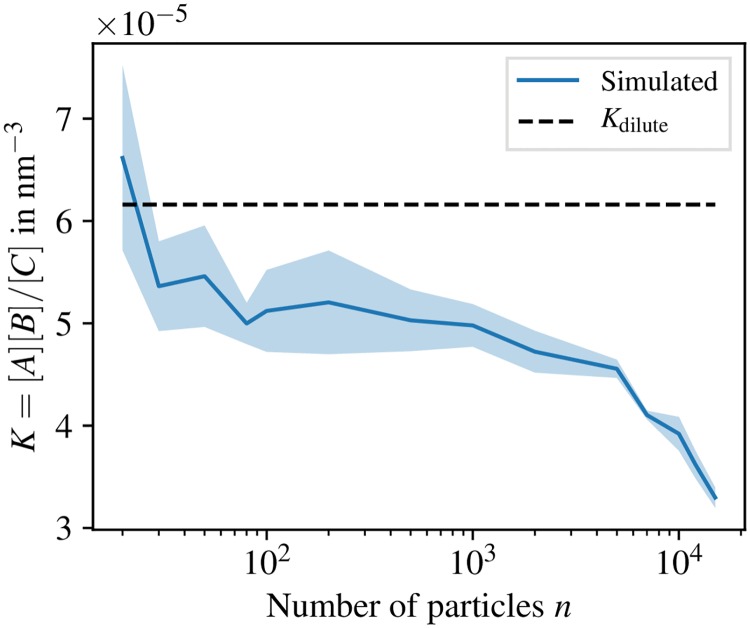
Fig 9. Equilibrium constant transition from dilute to dense systems.
The equilibrium constant K is obtained by simulation for different choices of the number of particles n = (NA + NB)/2 + NC which corresponds to a density due to constant volume of the simulation box and compared to an analytically obtained equilibrium constant of a dilute system (dashed line). The number of particles n remains constant during the course of a simulation. The shaded areas are standard deviations from the recorded data.