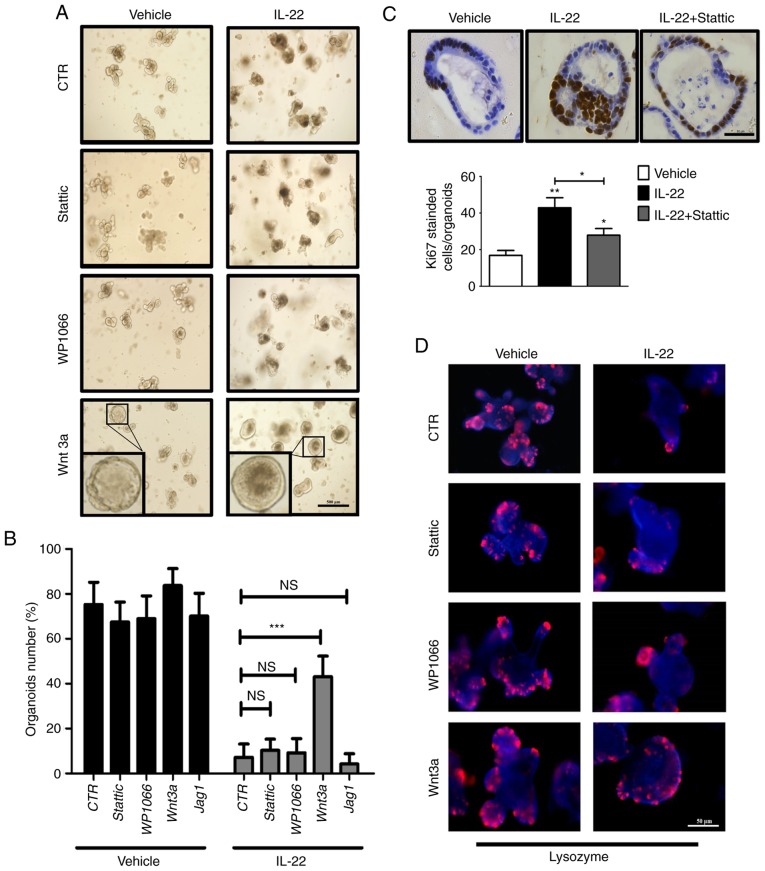
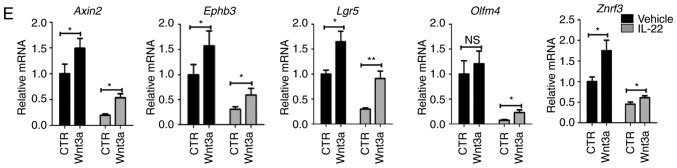
Figure 5.
Interleukin (IL)-22 causes defects in organoid formation mainly through the Wnt pathway. (A) Organoids were cultured for 2 days followed by treatment with various combinations of IL-22 (100 ng/ml), Wnt3a (200 ng/ml), WP1066 (5 μM) and Stattic (3 μM). Scale bar, 500 μm. The inset is the magnification of one representative organoid. (B) The number of organoids after 2 days of treatment with various combinations of IL-22, Wnt3a, WP1066, Stattic and Jag1 was counted. Data are the means ± SEM; and ***P<0.001 vs. Control (100 ng/ml IL-22 treatment group); NS, not significant; analyzed by one-way ANOVA. (C) Organoids were cultured for 2 days followed by treatment with various combinations of IL22 and Stattic. The expression of Ki67 was detected by immunohistochemical staining. Scale bar, 50 μm. The quantitative analysis is presented at the bottom panel. Data are the means ± SEM; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and vs. the vehicle; analyzed by one-way ANOVA. (D) Organoids were cultured for 2 days followed by treatment with various combinations of IL-22, Wnt3a, WP1066 and Stattic. The expression of Lysozyme (Paneth cell marker) was determined by immunofluorescence. Scale bar, 50 μm. (E) Organoids were cultured for 2 days followed by treatment with various combinations of IL-22 and Wnt3a. The expression of ISC markers (Lgr5, Olfm4 and Znrf3) and Wnt target genes (Axin2 and Ephb3) was examined by RT-qPCR. Data are the means ± SEM; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and vs. Control (the organoid cultured without IL-22) or Control (100 ng/ml IL-22 treatment group); analyzed by t-test.