Figure 6. RCD1 is involved in mitochondrial dysfunction, chloroplast ROS and PAP signaling pathways.
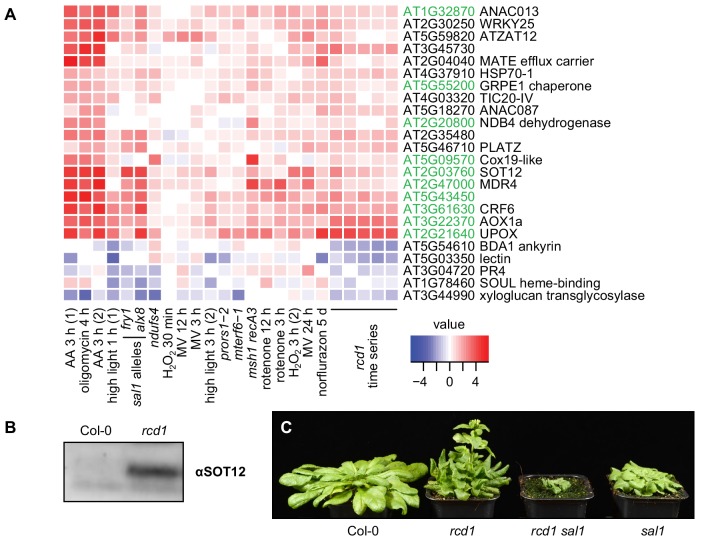
(A) Regulation of rcd1 mis-expressed genes under perturbations of organellar functions in the selected subset of genes. A complete list of rcd1-misexpressed genes is presented in Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Similar transcriptomic changes are observed between the genes differentially regulated in rcd1 and the genes affected by disturbed chloroplastic or mitochondrial functions. Mitochondrial dysfunction stimulon (MDS) genes regulated by ANAC013/ANAC017 transcription factors, are labeled green. (B) Sulfotransferase SOT12 encoded by an MDS gene accumulated in rcd1 under standard growth conditions, as revealed by immunoblotting with the specific antibody. (C) Phenotype of the rcd1 sal1 double mutant under standard growth conditions (12 hr photoperiod with white luminescent light of 220–250 µmol m−2 s−1).
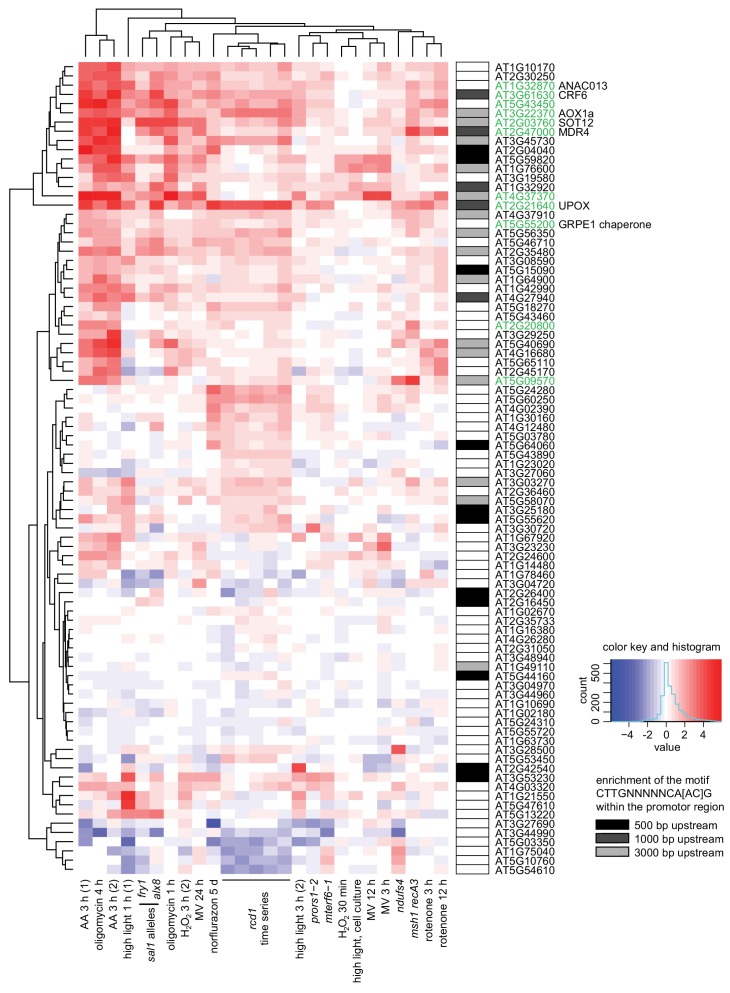
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Clustering analysis of genes mis-regulated in rcd1 (with cutoff of logFC <0.5) in published gene expression data sets acquired after perturbations of chloroplasts or mitochondria.
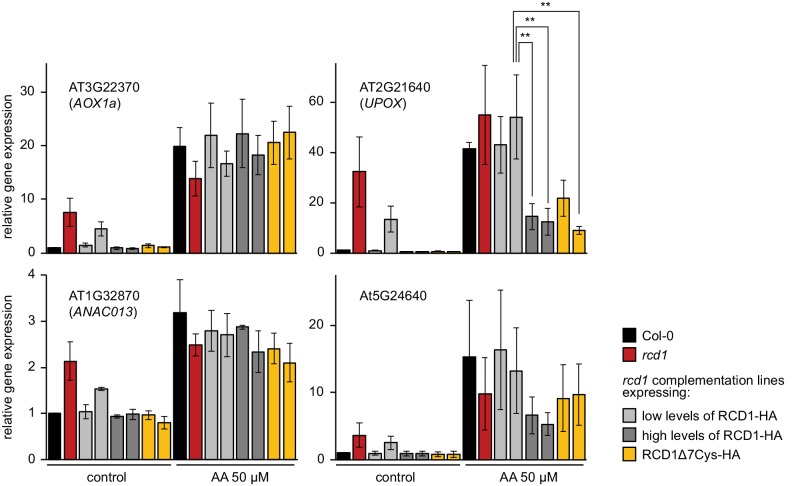
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Induction of MDS genes in rcd1 and rcd1 complementation lines.
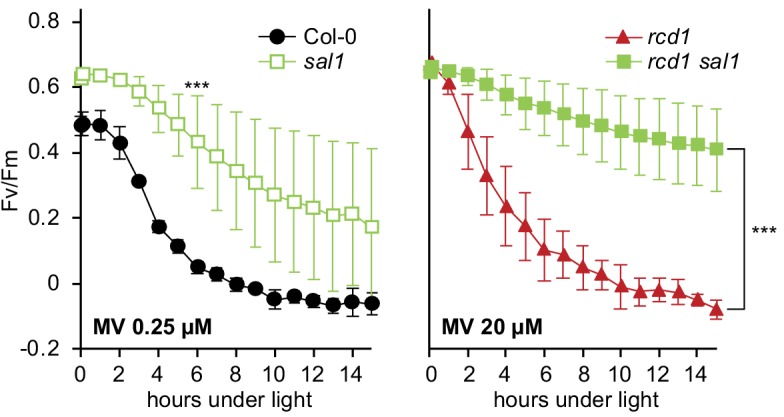
Figure 6—figure supplement 3. Tolerance of PSII to chloroplastic ROS in sal1 mutants.