Figure 3.
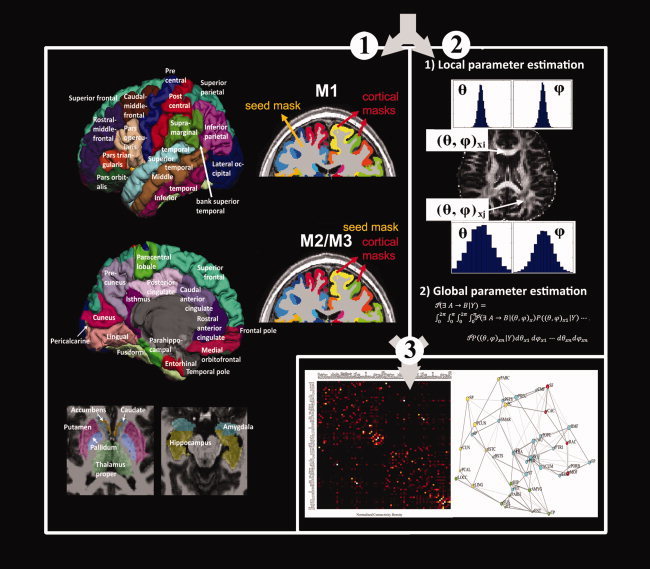
Procedure for reconstructing brain networks using diffusion probabilistic tractography. First, the T1‐weighted images were parcellated into 82 cortical and subcortical brain regions and seed masks located either in deep white matter (M1) or at the GM/WM interface (M2 and M3) were used for tractography (1); Second, probabilistic tractography implemented in FSL was used to derive the interregional connectivity map among different brain regions. The local orientation pdfs on each voxel were estimated, and then global connectivity was derived by sampling from the local pdfs. When a “probabilistic streamline” connected two different brain regions, it was counted and considered to contribute one unit to the total connectivity map (2). Lastly, interregional connectivity maps were derived based on the probabilistic tractography outputs. The topology of brain networks was reconstructed and analyzed using graph‐theoretic methods (3). [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
