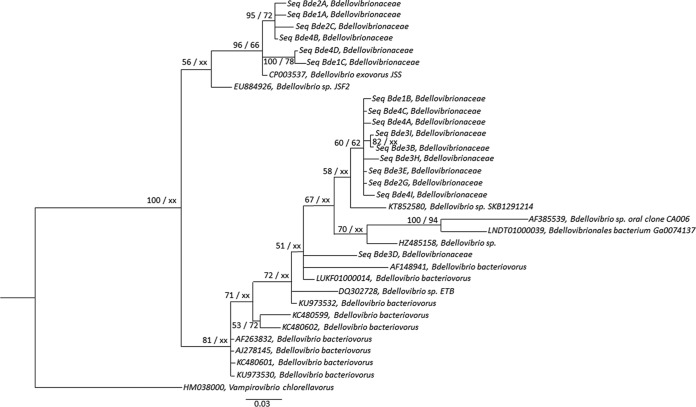
FIG 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of 16 centroid sequences of Bdellovibrionaceae from Lakes Annecy, Bourget, and Geneva based on 16S rRNA gene Sanger sequencing obtained after curation and clustering, along with 16 other sequences retrieved from Arb-SILVA (42), including two type species, Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and Bdellovibrio exovorus. All sequences were aligned using MUSCLE (66) via MEGA6 (60). The alignment was trimmed at both ends to eliminate gaps and then curated with Gblocks (68), resulting in 241 positions from 245 positions. The best-fit model of nucleotide substitution was selected using jModelTest-2.1.1 (69) through an Akaike model selection strategy, resulting in a TIM1+I+G model. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by the maximum likelihood method using PhyML-3.1 (71), and Bayesian inference (GTR+I+G) was conducted using MrBayes 3.2.6 (72) with 5 million generations and a burn-in value of 25%. Posterior probability (PP) values followed by bootstrap values are added to the left of a node when possible (PP/BS). Bootstraps below 50 were deleted. Accession numbers are listed to the left of some organism names. Vampirovibrio chlorellavorus was used as an outgroup to root the Bdellovibrionaceae tree.