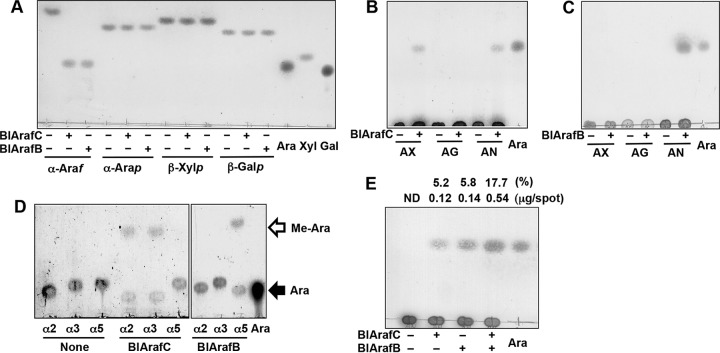
FIG 4.
Substrate specificities of BlArafC and BlArafB. The substrates were incubated with recombinant BlArafC or BlArafB at 37°C overnight and analyzed by TLC. (A) Action on synthetic substrates. α-Araf, pNP-α-l-arabinofuranoside; α-Arap, pNP-α-l-arabinopyranoside; β-Xylp, pNP-β-xylopyranoside; β-Galp, pNP-β-galactopyranoside; Ara, standard l-arabinose; Xyl, standard d-xylose; Gal, standard d-galactose. (B) Action of BlArafC on natural substrates. AX, arabinoxylan; AG, arabinogalactan; AN, arabinan; Ara, standard l-arabinose. (C) Action of BlArafB on natural substrates. (D) Action of BlArafC and BlArafB on synthetic disaccharide substrates. α2, Arafα1,2Arafα1-OMe; α3, Arafα1,3Arafα1-OMe; α5, Arafα1,5Arafα1-OMe; Ara, standard l-arabinose. (E) Synergy effect of coincubation of BlArafC and BlArafB on arabinan degradation. Arabinan was incubated with either BlArafC or BlArafB, or both. The amount of released l-arabinose was determined and the hydrolysis (in percent) of arabinan is shown above the panel. Ara, standard l-arabinose. ND, not detected. 1-Butanol–acetic acid–water (2:1:1, by volume) was used as a developing solvent in the assays whose results are shown in panels A to C and E; chloroform-methanol-acetic acid (6:1:1, by volume) was used in the assay whose results are shown in panel D.