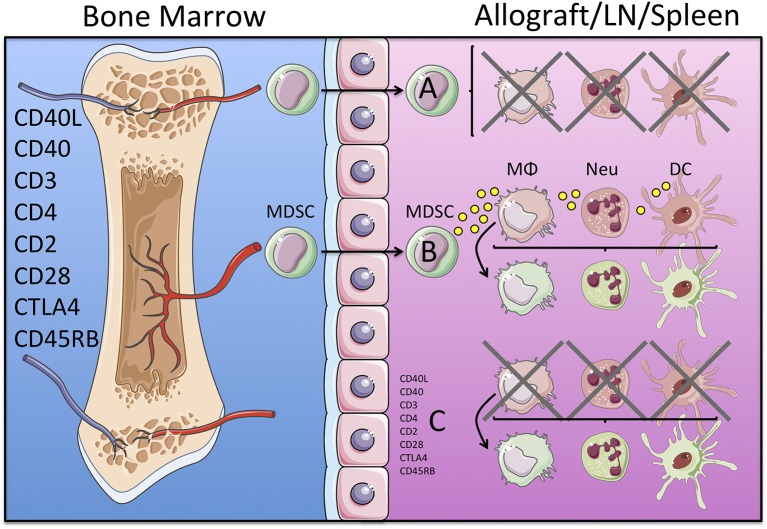
Figure 1.
Potential mechanisms of immune regulation mediated by MDSC in organ transplantation. Induction of transplantation tolerance in experimental murine models is achieved by targeting TCR and co-stimulatory blockade with monoclonal antibodies. These therapeutic treatments may induce the development of an MDSC precursor that leaves the bone marrow and may migrate into the allograft, lymph node (LN) and/or the spleen. Once in the tissue MDSC may mediate direct inhibition of immunogenic myeloid cells (macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells in red), as depicted in (A); or secrete cytokines and growth factors that convert immunogenic (red) into tolerogenic (green) myeloid cells, as depicted in (B). Alternatively, both processes (direct inhibition of immunogenic and/or conversion into tolerogenic myeloid cells) may be a direct effect of the tolerogenic regimen (monoclonal antibodies) independently of the MSDC, as depicted in (C).