Figure 5.
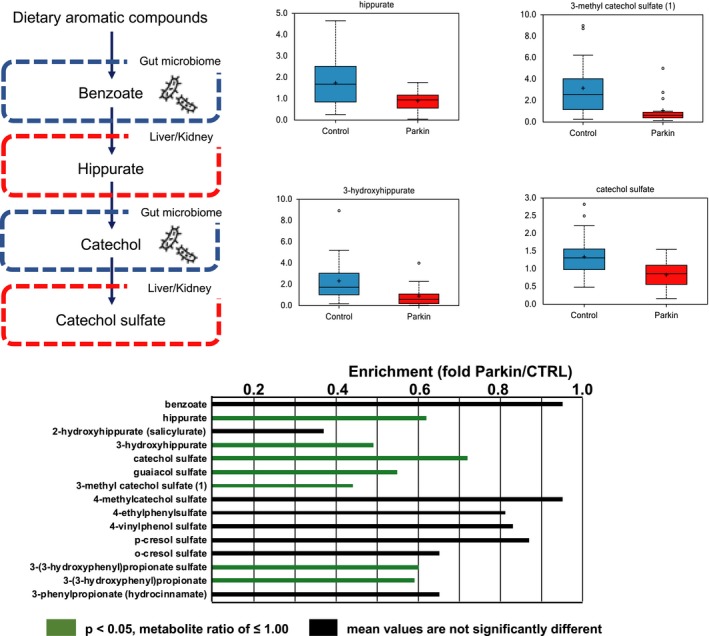
Alterations in benzoate and related metabolites in patients with parkin‐linked Parkinson's disease. Benzoate is produced from microbial degradation of dietary aromatic compounds in the intestine. The benzoate degradation pathway includes products of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan), as well as secondary bile acids, and is associated with microbial action in the gut. Significantly lower levels of benzoate and its metabolites were detected in patients than controls. Green (P < 0.05) columns indicate a significantly lower metabolite ratio and trending lower level of metabolites than controls, respectively. Black columns indicate no significant differences between patients and control subjects. Parkin, parkin‐linked Parkinson's disease.
