Figure 5.
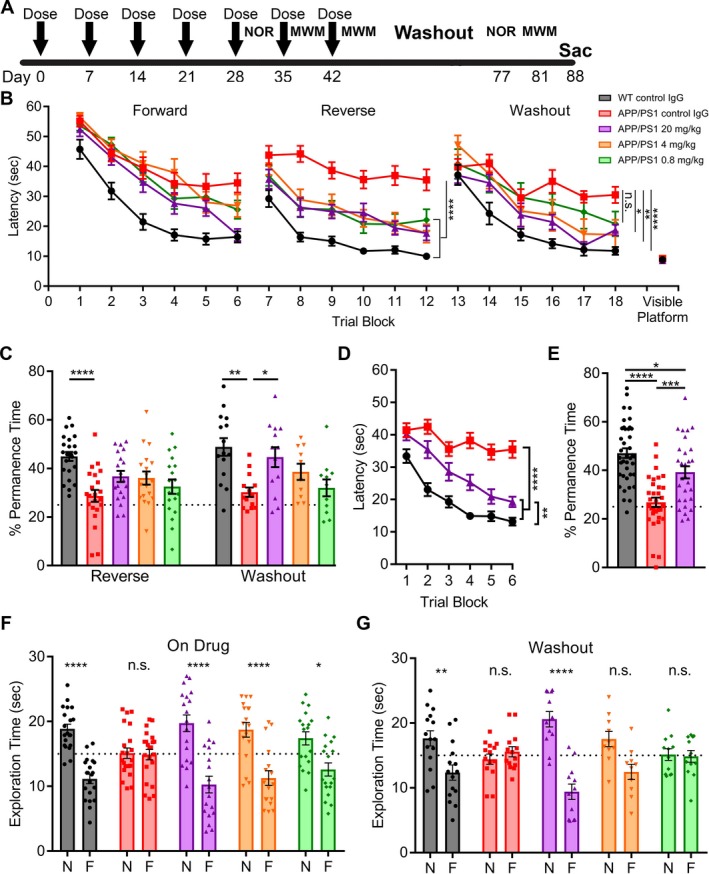
AZ59 reversal of learning and memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice is dose‐dependent and persists after washout. (A) Timeline of treatment and testing. WT and APP/PS1 mice (10–11 months old) were randomized into five groups receiving 20 mg/kg of control Ig, 0.8 mg/kg AZ59, 4 mg/kg AZ59 or 20 mg/kg AZ59 once weekly via i.p. injection. (B) After 5 weeks of treatment, mice completed the MWM twice with a forward and reverse set of 24 swims. The control IgG treated APP/PS1 group differed significantly from all other groups by one‐way RM‐ANOVA over the last twelve trials of the reverse swim with Tukey's post hoc multiple comparisons test (****,P < 0.0001). APP/PS1 mice receiving the two highest doses of AZ59 (4 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg) did not differ significantly from WT mice (P > 0.05), but those receiving the lowest dose (0.8 mg/kg) were slower than WT (*,P < 0.05). n = 18–26 per group. After 7 weeks of treatment, the mice entered a one‐month washout period. They then completed the MWM with the platform moved to a new quadrant. The control IgG treated APP/PS1 group differed significantly from all other groups except the 0.8 mg/kg group (P > 0.05) by one‐way RM‐ANOVA over the last twelve trials of the washout swim with Tukey's post hoc multiple comparisons test (*,P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001). APP/PS1 mice receiving the two highest doses of AZ59 (4 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg) did not differ significantly from WT mice (P > 0.05), but those receiving the lowest dose (0.8 mg/kg) were slower than WT (*,P < 0.05). n = 10–15 per group. All data are mean ± SEM. (C) 24 h after the reverse and washout swims the mice completed a probe trial. WT mice spent significantly more time in the target quadrant than control APP/PS1 mice. APP/PS1 mice receiving 20 mg/kg AZ59 showed a trend to perform better than those receiving control IgG, but the difference was not significant (P = 0.069). (****,P < 0.0001), n = 18–26 per group. For the washout probe trial, APP/PS1 mice receiving 20 mg/kg AZ59 and WT mice spent significantly more time in the target quadrant than did control APP/PS1 mice (*,P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). n = 10–15 per group. All data are mean ± SEM, one‐way ANOVA with Dunnett's comparison to APP/PS1 control IgG. (D) Meta‐analysis of the final block of swims each mouse receiving WT control IgG, APP/PS1 control IgG, or APP/PS1 20 mg/kg AZ59 performed. WT and APP/PS1 mice receiving 20 mg/kg AZ59 performed significantly better by one‐way RM‐ANOVA over the last twelve trials with Tukey's post hoc multiple comparisons test (****, P < 0.0001). WT mice also performed significantly better than APP/PS1 mice receiving 20 mg/kg AZ59 (**,P < 0.01). n = 32–39 per group, all data are mean ± SEM. (E) Meta‐analysis of the final probe trial for each mouse receiving WT control IgG, APP/PS1 control IgG, or APP/PS1 20 mg/kg AZ59 was performed. WT and APP/PS1 mice receiving 20 mg/kg AZ59 spent significantly more time in the target quadrant than APP/PS1 mice receiving control IgG (***,P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). WT mice performed significantly better than APP/PS1 mice receiving 20 mg/kg AZ59 (*,P < 0.05). One‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc multiple comparisons test, n = 32–39 per group, all data are mean ± SEM. (F) After 5 weeks of treatment, mice completed the NOR test. APP/PS1 mice receiving AZ59 and WT mice preferred to interact with the novel object (*,P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001), while APP/PS1 mice receiving control IgG did not (P > 0.05). N, novel object; F, familiar object. Analysis by two‐way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparisons test. n = 18–26 per group, data are mean ± SEM. The dashed line indicates an equal amount of time spent with either object. (G) After washout, APP/PS1 mice receiving 20 mg/kg AZ59 and WT mice preferred to interact with the novel object (**,P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001), while APP/PS1 mice receiving control IgG or 4 or 0.8 mg/kg AZ59 did not (P > 0.05). N, novel object; F, familiar object. Analysis by two‐way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparisons test. n = 10–15 per group, data are mean ± SEM. The dashed line indicates an even amount of time spent with either object.
