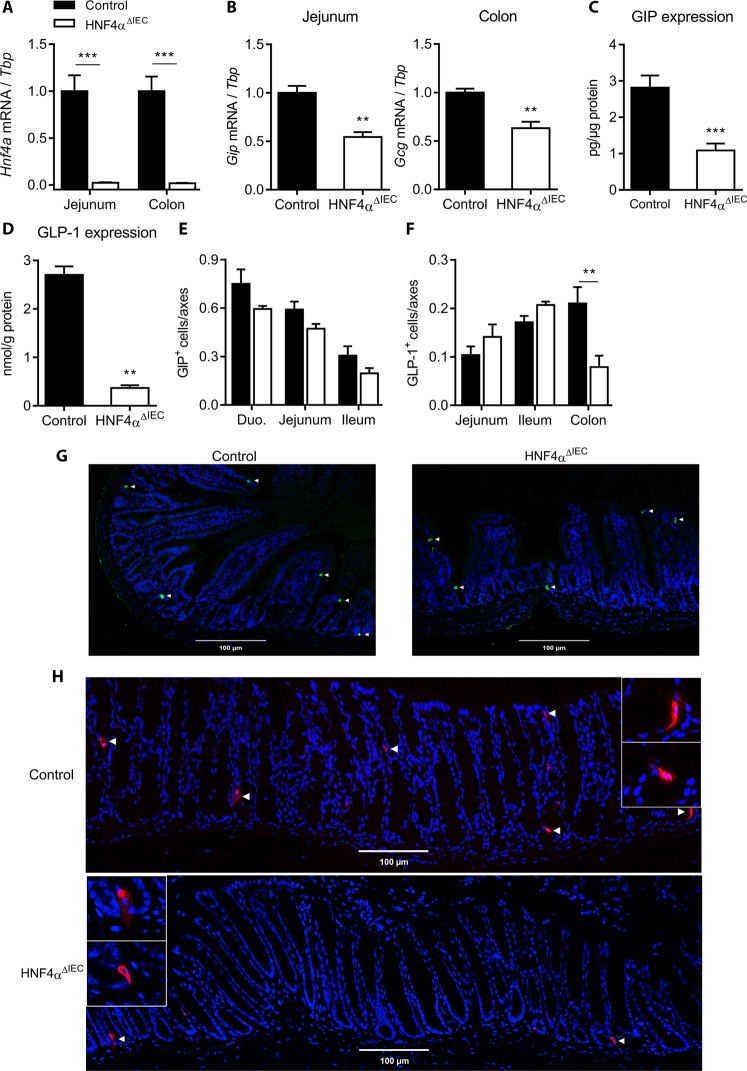
Figure 1.
HNF4α regulates GIP and GLP-1 expression in the mouse intestine. (A) Hnf4a gene expression relative to Tbp measured in the jejunum and colon of 1 week-old control (black columns) and HNF4αΔIEC (white columns) mice (n = 4–6). (B) Gip and Gcg gene expression relative to Tbp measured in the jejunum and colon of control (black columns) and HNF4αΔIEC (white columns) mice (n = 4–8). (C) GIP protein level quantified by ELISA in the jejunum of control (black columns) and HNF4αΔIEC (white columns) mice (n = 5–10). (D) GLP-1 protein level quantified by ELISA in the colon of control (black columns) and HNF4αΔIEC (white columns) mice (n = 5–10). Enteroendocrine cells immunopositive for GIP (E) or GLP-1 (F) were counted per crypt-villus axes along the intestinal tract from both control (black columns) and HNF4αΔIEC (white columns) mice (n = 3). Representative immunostaining of enteroendocrine cells expressing GIP in the duodenum (G) and GLP-1 in the colon (H) of control and HNF4αΔIEC mice.