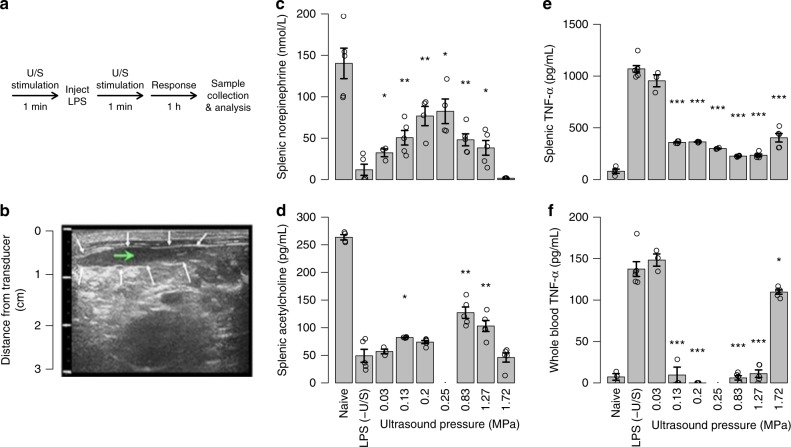
Fig. 2.
Splenic U/S neuromodulation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP). a The timeline of the U/S neuromodulation performed in the LPS-induced inflammation model (see Methods and Supplementary Figures 1–6 for details; stimulation parameters were 1.1 MHz, 136.36 µs pulse length, and 0.5 ms pulse repetition period). b Example U/S image of the spleen used to locate the U/S stimulus (white arrows—outline of the spleen; green arrow—target point for U/S stimulation). c–e Splenic concentrations of CAP signaling molecules, including norepinephrine (c), acetylcholine (d), and TNF (e) are shown for naive animals, sham controls (LPS, -U/S), and with U/S stimulation (0.03–1.72 MPa). f Whole-blood concentrations of TNF for the same conditions as (e). The asterisks mark statistical significance using two-sided t-test versus LPS only controls (with p-value thresholds; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). n = 5 for all experiments in this figure except for all LPS − (U/S) controls which were n = 7