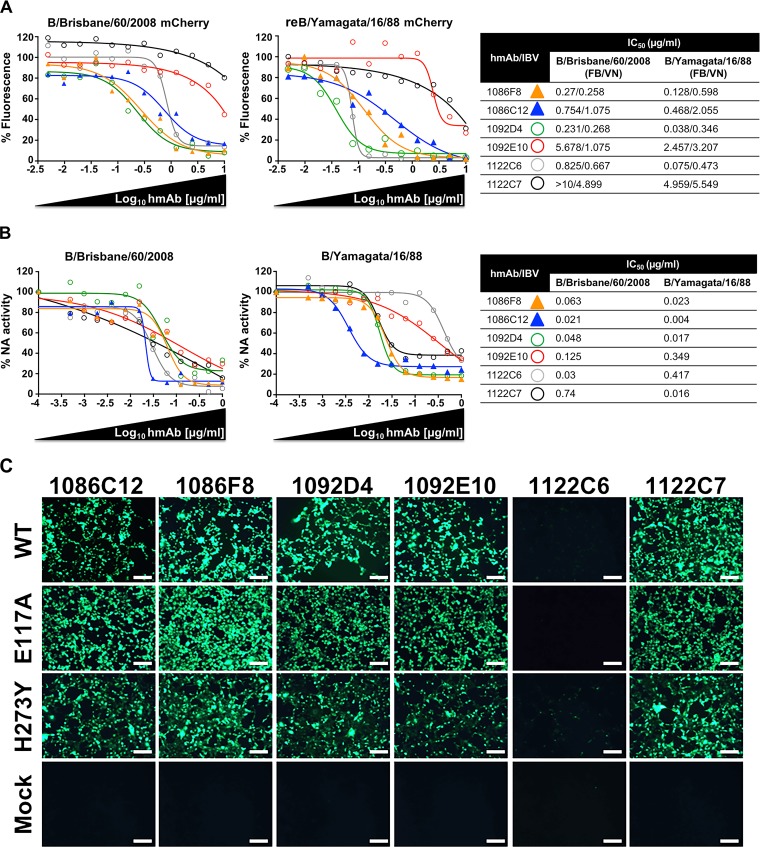
FIG 3.
Ability of IBV NA-specific hMAbs to inhibit viral infection and NA activity. (A) Fluorescence-based microneutralization assay. MDCK cells were infected with the indicated mCherry-expressing virus (B/Brisbane/60/2008 or reB/Yamagata/16/1988) and then incubated with 2-fold serial dilutions (starting concentration, 10 µg/ml) of the IBV NA-specific hMAbs. Virus neutralization was evaluated and quantified using a fluorescence microplate reader, and the percentage of infectivity was calculated using sigmoidal dose response curves. Mock-infected cells and viruses in the absence of hMAb were used as internal controls. Percentages of inhibition were normalized to infection in the absence of hMAb. Data show means of the results determined in triplicate. IC50 data corresponding to the IBV NA hMAbs were determined using a fluorescence-based assay (FA) or a traditional viral neutralization assay (VN) and mCherry-expressing or WT viruses, respectively. (B) IBV NA-specific hMAbs inhibit NA enzymatic activity. B/Brisbane/60/2008 or B/Yamagata/16/1988 WT viruses were preincubated with 2-fold serial dilutions of the IBV NA-specific hMAbs, and NA activity was determined at 18 h postincubation on fetuin-coated plates. Data represent mean percentages of virus-alone NA activity from duplicate wells. The percentage of activity and the IC50 were calculated using sigmoidal dose response curves. (C) IBV NA hMAbs recognize IBV oseltamivir resistance mutations. MDCK cells were infected (MOI of 0.1) with the indicated WT and NA (E117A and H273Y) viruses, and hMAb binding (1 μg/ml) was evaluated by IFA. Bar, 100 µm.