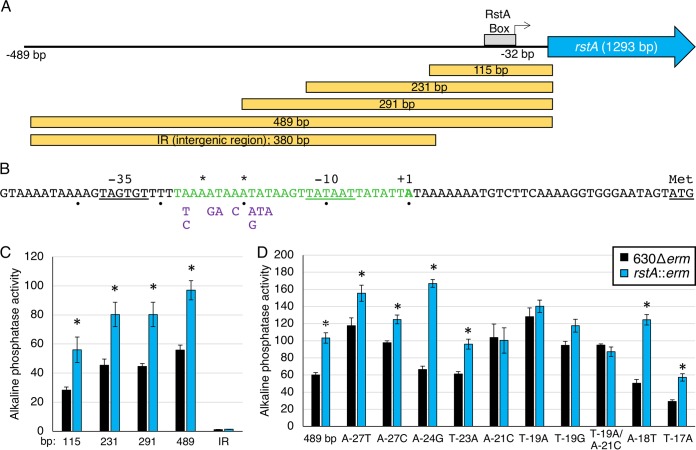
FIG 1.
RstA controls its gene expression through an inverted repeat sequence overlapping the rstA promoter. (A) A schematic of the rstA promoter region denoting the general location of the putative RstA box, the transcriptional start (32 bp upstream from the start codon; represented by the bent arrow), and the rstA open reading frame (not to scale). The yellow boxes indicate the locations and sizes of promoter fragments constructed for the phoZ reporter fusions in panel C. (B) The rstA promoter, marked by +1, overlaps a 29-bp imperfect inverted repeat (shown in green). The asterisks above the sequence mark the mismatched nucleotides within the inverted repeat. The −10 and −35 consensus sequences and the ATG start codon are underlined. The nucleotides below the sequence represent the substitutions tested in panel D. (C and D) Alkaline phosphatase (AP) activity of the PrstA::phoZ reporter fusions of various lengths, including the upstream intergenic region (IR) (−489 bp to −112 relative to the translational start) of rstA (C) (PrstA115 [MC979/MC980]), PrstA231 [MC1010/MC1011], PrstA291 [MC1012/MC1013], PrstA489 [MC773/MC774], PrstAIR [MC1008/MC1009]) or of the full-length PrstA::phoZ promoter with various nucleotide substitutions (D) (PrstA489 [MC773/MC774], PrstAA-27T [MC830/MC831], PrstAA-27C [MC856/MC857], PrstAA-24G [MC858/MC859], PrstAT-23A [MC832/MC833], PrstAA-21C [MC860/MC861], PrstAT-19A [MC834/MC835], PrstAT-19G [MC862/MC863], PrstAT-19A/A-21C [MC1433/1434], PrstAA-18T [MC836/MC837], PrstAT-17A [MC838/MC839]) in strain 630Δerm and the rstA::erm mutant (MC391), respectively, grown on 70:30 sporulation agar at H8. The means ± standard errors of the means for four biological replicates are shown. Values that are significantly different (P < 0.05) by Student’s t test from the activity observed for the 630Δerm parent strain for each promoter construct are indicated by an asterisk.