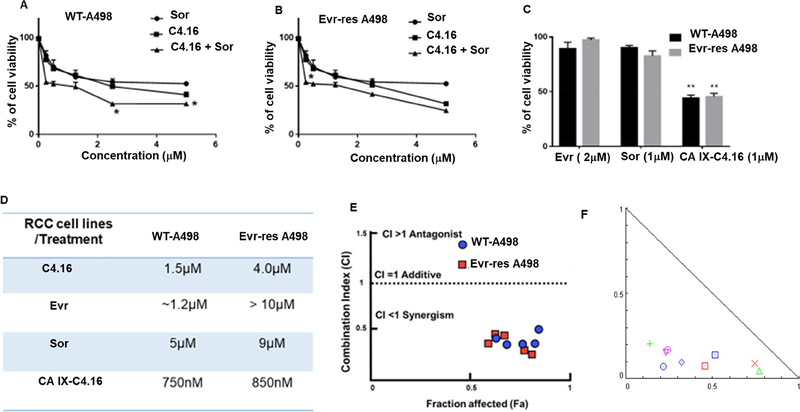
Figure 4. C4.16 and CA IX-C4.16 are more efficient in inhibiting the growth of WT and Evr-res A498 cells.
In vitro cytotoxicity assay of C4.16 and Sor on (A) WT and (B) Evr-res A498 indicates C4.16 was more potent than the FDA approved drug, Sor and combining both drugs C4.16+Sor demonstrated significantly lower cell viability. (C) The results also showed that CA IX-C4.16 is more effective in inhibiting the growth of A498 (WT and Evr-res) RCC cell lines compared to Sor and Evr and support the notion that C4.16 is more potent than FDA approved drugs in the RCC model. (D) Summary of IC50 value for all the tested drugs with the tested RCC cell lines are shown in a tabular fashion. The data in the IC50 columns represent the mean of three independent experiments. Indicated A498 WT and their respective Evr-res A498 cells were either untreated (control) or treated with a noted dose of C4.16, Sor, Evr, and CA IX-C4.16 for 48 h. (E) High synergistic CI value of C4.16 in combination with Sor supports the hypothesis of selecting the combination to treat RCC for reversing the drug resistance. This data builds a rationale for using hypoxic core penetrating CA IX-C4.16+Sor to sensitize the drug resistant RCC. (F) Isobologram of CA IX-C4.16+Sor suggests high synergism combination treatment in RCC cells.