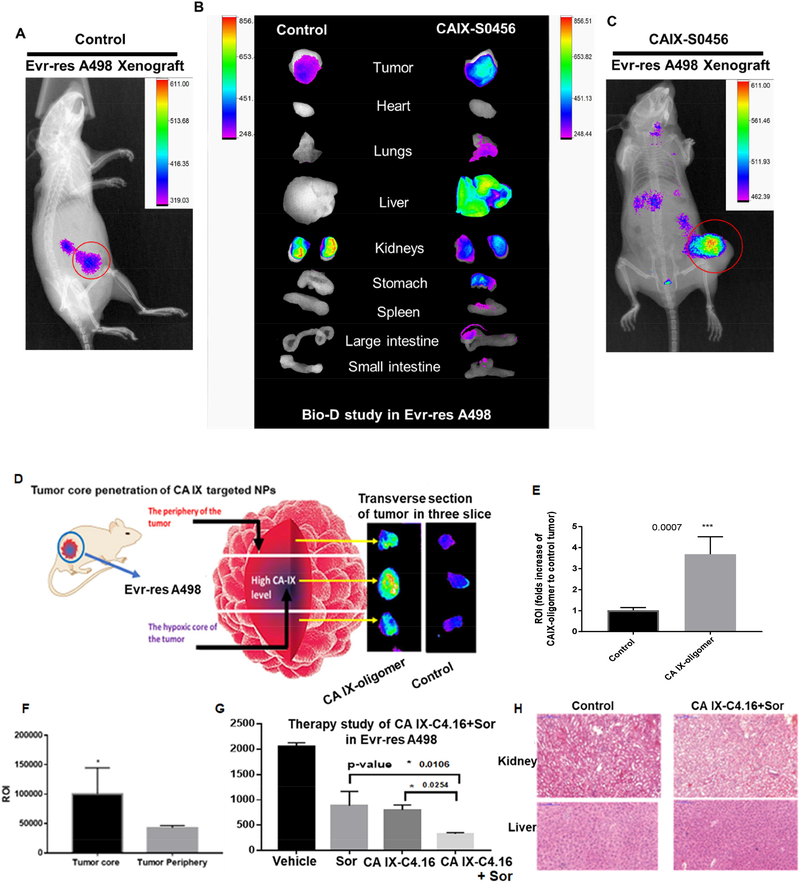
Figure 7: Superior tumor specificity of CA IX-oligomer and combination antitumor efficacy study in Evr-res A498 xenograft RCC model.
(A and C) Superior tumor accumulation of CAIX oligomer (CA IX-S0456) as compared to control (S0456) in Evrres A498 tumor xenograft model is shown. (B) Biodistribution (Bio-D) study of CA IXS0456 showed superior tumor specificity and low non-specific liver uptake in Evr-res A498 tumor bearing mice. The control, S0456 showed poor tumor accumulation with high off-target activity. (D) Further to demonstrate the tumor core penetration of NIR dye, the isolated Evr-res A498 tumor was transversely sectioned into 3 parts; the brightest fluorescence intensity at the middle (core) section confirmed the excellent hypoxic tumor core penetration ability of CA IX-S0456 compared with non targeted control. (E) Significantly high tumor accumulation (more than 3-fold) of CA IX-oligomer compared to control suggests the high tumor specificity of the oligomer. (F) Quantification of fluorescent ROI indicates CA IX-oligomer had significantly high tumor core penetration and accumulation as compared to its periphery. The results suggest the importance of CA IX-oligomer in selective RCC tumor targeting ability. (G) CA IXC4.16+Sor showed significant tumor growth inhibition compared to vehicle(control), Sor, and CA IX-C4.16 in Evr-res A498 xenograft tumor. The remarkable tumor growth suppression of combination therapy supports the rationale of using CA IX targeting nano-formulation as the delivery vehicle of potent drugs such as C4.16. The data is represented as average values from four animals in the respective group, bars, SE, significant where *p<0.05 vs. Control. (H) Histopathologic (H&E staining) examination was done to determine the toxicity of therapeutic drugs on livers and kidneys at the end of the experiments. The images indicate that there is no significant sign of necrosis or loss of tissue architectural in vehicle control and CA IX-C4.16+Sor treated tissues indicating safety of the formulations.