Fig. 5.
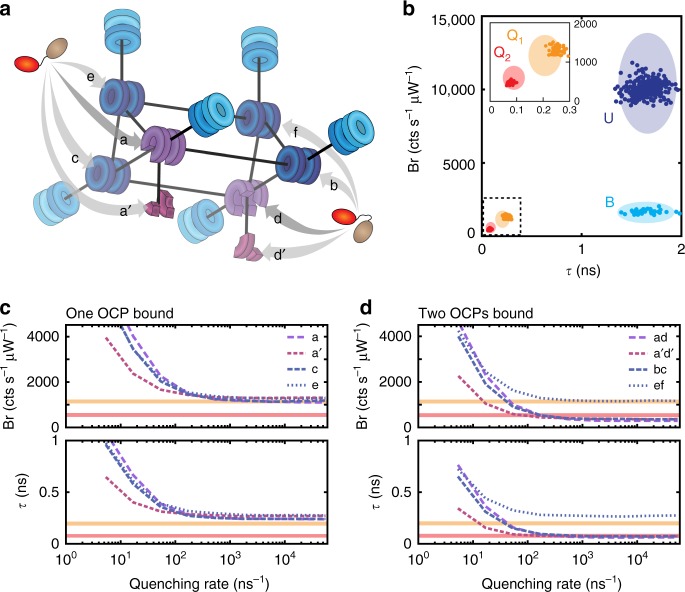
Compartmental model of OCP-quenched CB-PB phycobilisome for one and two quenchers. a Schematic structure and connectivity of compartmental CB-PB model, after van Stokkum et al.61. All components are colored and positioned according to the structure shown in Fig. 1. Eight possible quenching sites for OCP are labeled (a–f, plus a′ and d′). b Scatter plot of brightness vs. fluorescence lifetime simulation results for four model conditions: unquenched (U), C-PC hexamer only (B), one OCP bound at site a, a′, or c (Q1), or two OCPs bound at site combinations ad, a’d’, or bc (Q2), with an assumed quenching rate of 540 ns−1 for each OCP compartment. Ellipses show the locations of the 95% confidence intervals for the four experimentally measured states U, B, Q1, and Q2, as originally depicted in Fig. 3c. c Brightness and fluorescence lifetime of the CB-PB phycobilisome for the case of one bound quencher located at each of the four rotationally unique sites a, a′, c, and e, plotted for increasing quencher strength. d Brightness and fluorescence lifetime of the CB-PB phycobilisome for two bound quenchers at each of the four unique pairs of C2-symmetric sites ad, a′d′, bc, and ef, plotted for increasing quencher strength. Horizontal lines in c and d show the experimentally measured parameters for Q1 (orange) and Q2 (red)