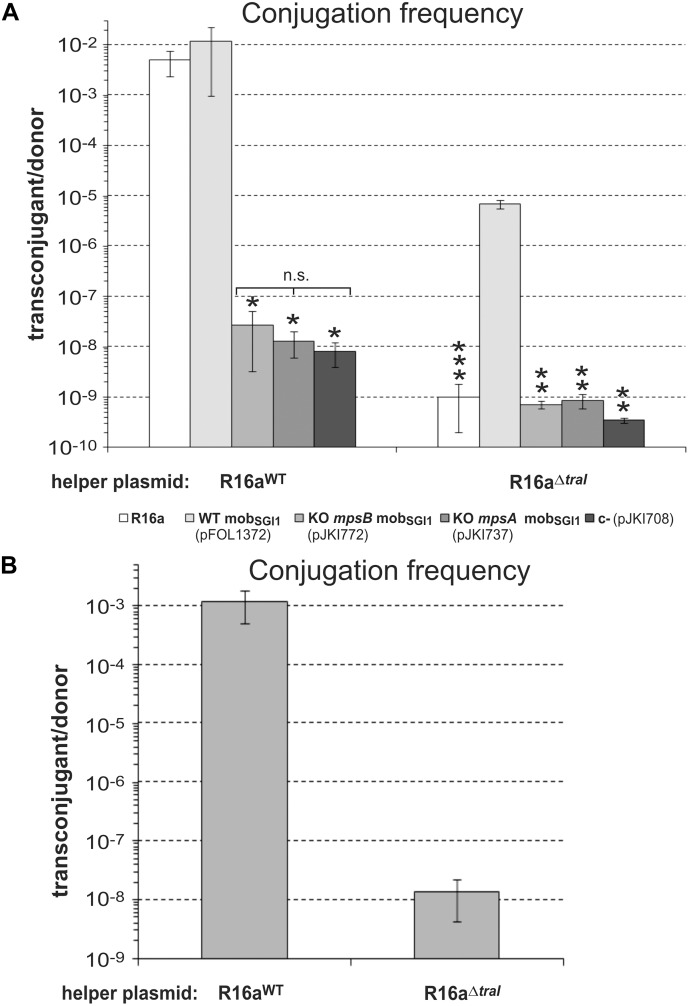
FIGURE 4.
The role of mpsA, mpsB and the helper encoded relaxase traI in SGI1 mobilization. (A) Transfer frequency of the p15A-based plasmids, containing WT (pFOL1372), KO mpsB (KO S019, pJKI772) and KO mpsA (KO S020, pJKI737) mobSGI1 regions was assayed in the presence of the WT or relaxase KO mutant helper plasmid R16a. For mating, TG1Nal donor and TG90 recipient E. coli strains were used. The bars show means of 4 independent experiments except those representing the transfer rate of the helper plasmids. Since the conjugation frequency of the helper plasmids was the same independently of the test plasmids, the transfer rate of the helper plasmids R16aWT and R16aΔTraI correspond to the mean of their transfer frequencies in the 4 different settings that have been repeated 4 times. ∗Transconjugants indicated by an asterisk carried also the helper plasmid (co-transfer was ∼100 %) suggesting that the transfer of test plasmids did not derive from regular trans-mobilization. ∗∗Transfer frequency was below the detection limit (transconjugants were not obtained). ∗∗∗Transfer frequency of R16aΔTraI was close to the detection limit, 6 transconjugant colonies were obtained from five independent experiments (mean frequency was ≤ 1.9 × 10-9). These colonies did not contain test plasmid. (B) Mobilization of SGI1-CWT by the helper plasmids R16aWT and R16aΔTraI from TG1Nal::SGI1-C donor into TG90 recipient strain.