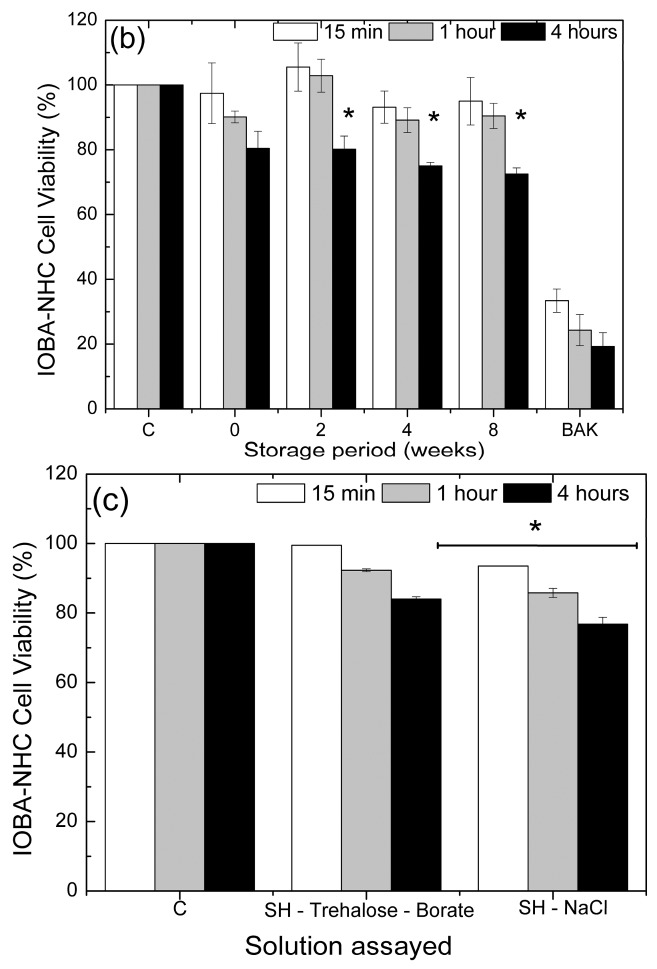
Figure 4.
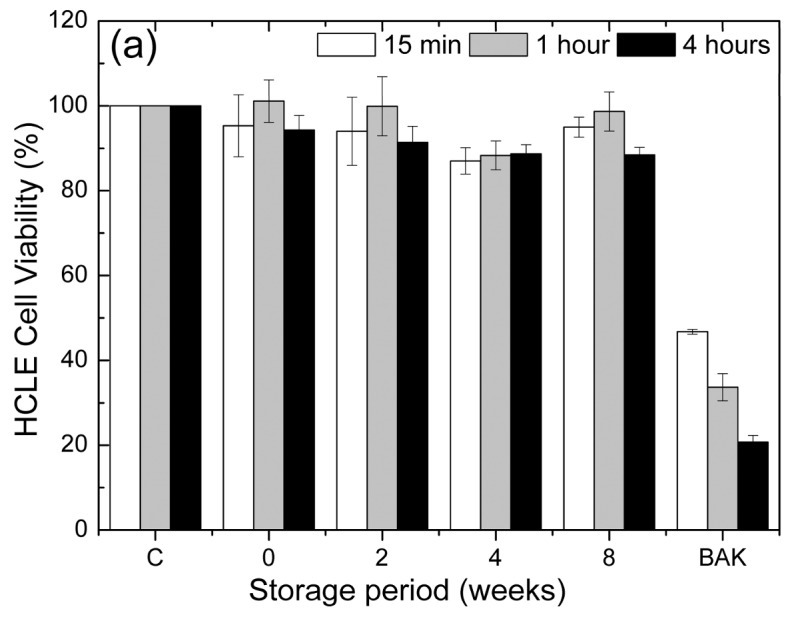
Viability of human corneal-limbal epithelial (HCLE) cells and Institute for Applied Ophthalmobiology normal human conjunctiva (IOBA-NHC) cells exposed to control and liposome formulations. The study was performed with freshly prepared FLFs and after storage for 2, 4, and 8 weeks at 4 °C in the dark. Exposure times were 15 min, 1 h, and 4 h. C, untreated cells were used as negative control; 0, FLF freshly prepared; 2, FLF stored for two weeks; 4, FLF stored for four weeks; 8, FLF stored for eight weeks; BAK, 0.005% benzalkonium chloride was used as the positive control. (a) For HCLE cells, there were no significant differences in viability among the different storage times and exposure times; (b) For IOBA-NHC cells, storage for 2, 4, and 8 weeks reduced the viability of cells exposed for four hours * p < 0.01 compared to the FLFs stored for the same period; (c) Cell viability of IOBA-NHC cells exposed to control and different solutions employed for liposomal dispersion. Exposure times were 15 min, 1 h, and 4 h. C, untreated cells were used as negative control; SH-trehalose-borate, a vehicle composed of sodium hyaluronate, trehalose, and borate-buffered solution used in the liposome dispersal in the present work; SH-NaCl, a vehicle composed of sodium hyaluronate (SH) and sodium chloride that was used to disperse liposomes in a previous work [19]. Neither vehicle in these experiments contained liposomes. Results were normalized to the viability of untreated cells. For C, the error bars were too small to be seen clearly. * p < 0.05 compared to untreated cells and to SH-trehalose-borate-treated cells at the same exposure time.