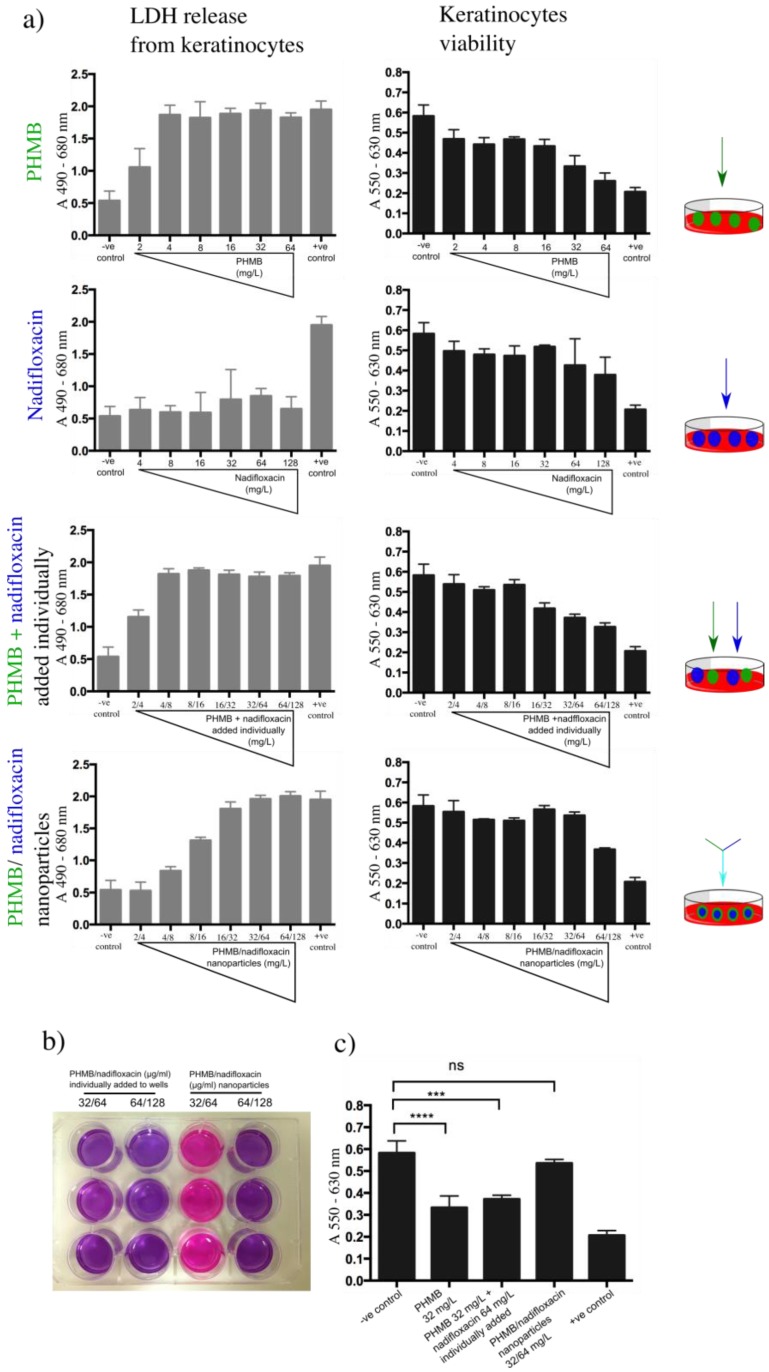
Figure 7.
Toxicity effects of nanoparticles towards keratinocytes. Keratinocytes were exposed to increasing concentration of PHMB or nadifloxacin, alone and in combinations. The combinations were either added individually to the wells or formulated as nanoparticles. (a) The toxicity assessment was based on the amount of LDH released by keratinocytes, followed by evaluation of cell viability using resazurin assay. Untreated cells were used as the base for LDH released by the cells and for viability resazurin assay (negative control). Cells treated with 0.5% Triton-X 100 were used as the positive control. (b) Image taken on cells exposed to different antimicrobial formulation and subjected to resazurin assay. The color of resazurin added into the cells treated with 32 mg/L of PHMB and 64 mg/L nadifloxacin added individually into the wells (column 1) remained purple indicates cell death. As expected, the same was observed with higher concentrations of PHMB (64 mg/mL) and nadifloxacin (128 mg/mL) (column 2). The same effects were observed when cells were treated with PHMB alone at 32 mg/mL (image is not shown). (c) Statistical analysis on the viability of the cells when exposed to 32 mg/L of PHMB alone, individually added with nadifloxacin or pre-formulated as nanoparticles. No significant difference in cell viability when treated with PHMB/nadifloxacin nanoparticles at 32 mg/L compared to the non-treated cells. Error bars represent standard deviations. *** (p ≤ 0.001), **** (p ≤ 0.0001), ns (not significant).