Table 1.
Representative post-polymerization reactions that can be used for the functionalization of polymers [42,44].
| Classification | Reaction scheme | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| Thiol-ene addition: The anti-Markovnikov addition of thiols to alkenes is facilitated by a radical source or by UV irradiation. |
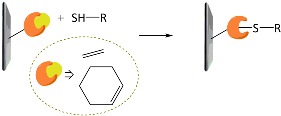
|
[45,46] |
| Thiol-disulfide exchange: This type of reaction is frequently found in biological systems. Disulfides as pyridyl disulfide are readily exchanged in high yields with thiol compounds. |
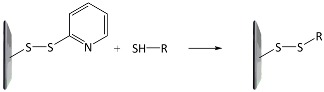
|
[47,48] |
| Epoxides, anhydrides, isocyanates: These are a class of reactive groups, that are, importantly, tolerant toward radical-based polymerization methods. |
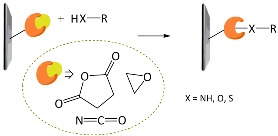
|
[49,50,51] |
| Ketones and aldehydes: These can selectively react with primary amines, alkoxyamines, and hydrazines, producing imines, oximes, and hydrozones, respectively. |
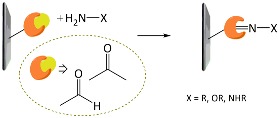
|
[52,53] |
| Active esters: The reaction of active ester groups with amines can proceeds selectively even in the presence of weaker nucleophiles, such as alcohols. |
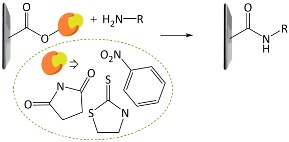
|
[54,55,56] |
| Diels–Alder cycloaddition: A diene and a substituted alkene can make cycloaddition reaction, which is reversible. |
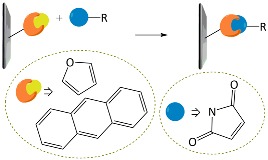
|
[57,58] |
| Michael addition: Thiols undergo Michael-type addition to activated alkenes, which proceeds rapidly in aqueous media under mild conditions. |
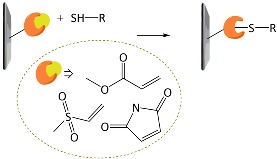
|
[59,60,61] |
