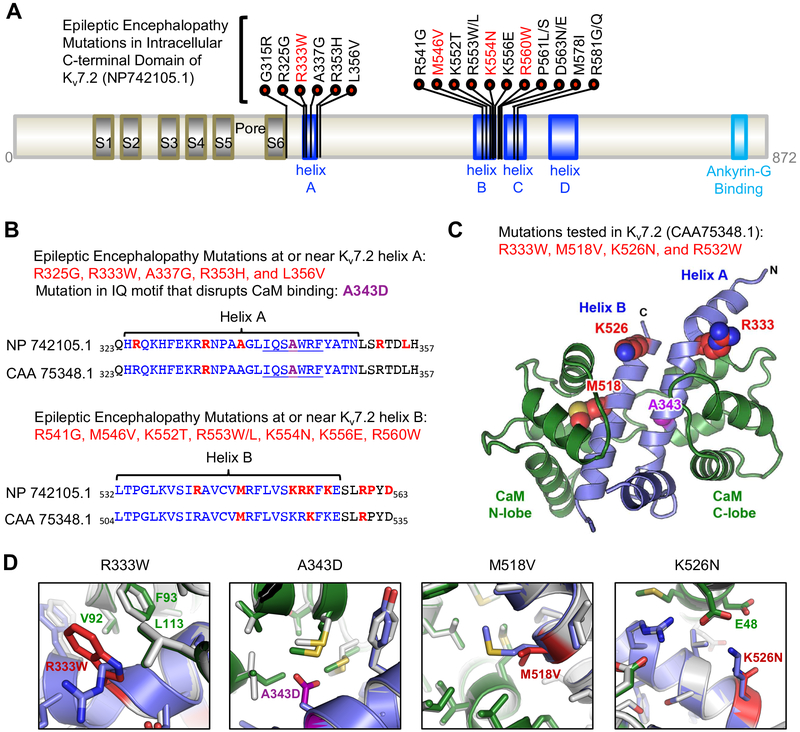
Figure 1. Distribution of epileptic encephalopathy mutations in CaM binding helices A and B of Kv7.2.
(A) Kv7.2 protein (NP_742105.1) showing functional domains including transmembrane S1–S6, a pore, an intracellular C-terminal tail containing helices A-D and ankyrin-G binding motif. Missense epileptic encephalopathy mutations are concentrated in helix A (residues 324–350), helix B (residues 532–557) and the linker between helix B and helix C (residues 568–589). The mutations (R333W, M546V, K554N) characterized in this study (red) are shown. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of Kv7.2 (NP_742105.1) and a shorter Kv7.2 isoform (CAA_75348.1 used in this study) showing helices A and B (blue), CaM-binding consensus IQ motif in helix A (underlined), A343D mutation (purple), and epileptic encephalopathy mutations (red). (C) Amino acids (R333, M518, K526) mutated in epileptic encephalopathy and characterized in this study (red) are shown on a model of Kv7.2 helices A and B (blue) in complex with Ca2+-bound CaM (green). A343 (purple) is located in helix A at the CaM C-lobe contact. R532 (not shown) is located distal to the helix B of this structure. (D) The modeled structure of wild type Kv7.2 helix A-B (blue) bound to Ca2+-bound CaM (green) is overlaid with the lowest energy model of the mutant Kv7.2 helix A-B (mutations in red) complexed with Ca2+-bound CaM (grey).