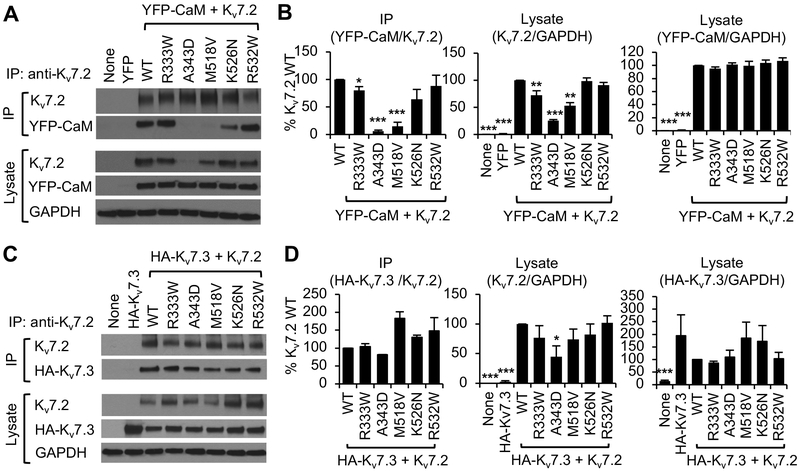
Figure 2. Kv7.2 expression and binding to apoCaM is impacted by epileptic encephalopathy mutations.
(A, B) Co-immunoprecipitation of YFP-CaM with wild type Kv7.2 (WT) or Kv7.2 containing epileptic encephalopathy mutations from transfected HEK283T cells. (A) Representative immunoblots. (B) Quantification of co-immunoprecipitation and lysate from 7 independent experiments: untransfected (None: n=6), YFP-CaM (n=6), YFP-CaM cotransfection with WT (n=7), R333W (n=7), A343D (n=6), M518V (n=7), K526N (n=6), or R532W (n=5). (C, D) Co-immunoprecipitation of Kv7.3 containing extracellular HA tag (HA-Kv7.3) with Kv7.2 WT or mutant Kv7.2 containing epileptic encephalopathy mutations from transfected HEK283T cells. (C) Representative immunoblots. (D) Quantification of co-immunoprecipitation and lysate from 6 independent experiments: untransfected cells (None: n=6), or cells transfected with HA-Kv7.3 (n=6), HA-Kv7.3 and Kv7.2 WT (n=6), R333W (n=6), A343D (n=4), M518V (n=5), K526N (n=5), or R532W (n=5). GAPDH served as a loading control. Data shown represent the Ave ± SEM (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005).