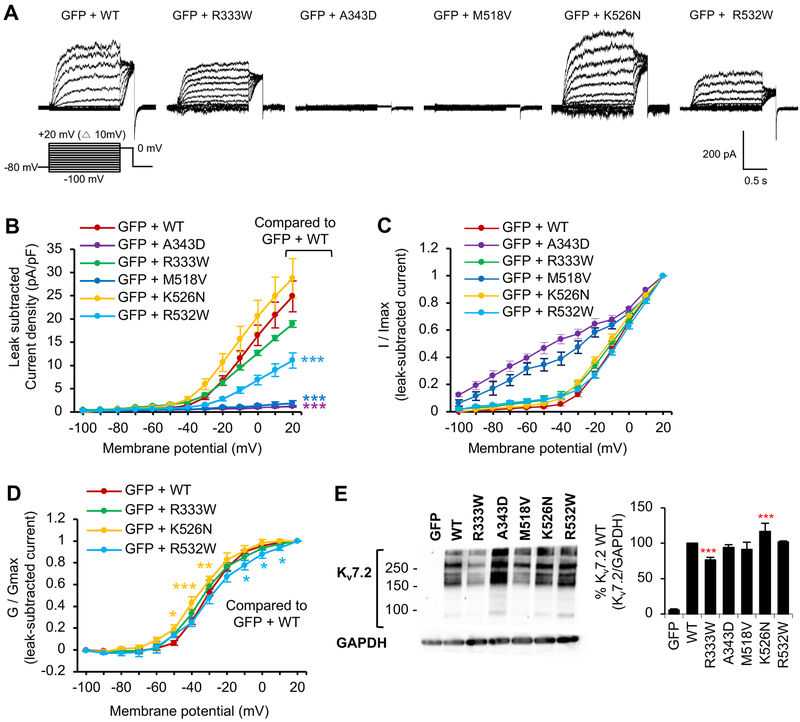
Figure 4. Voltage-dependent activation of Kv7.2 channels is decreased by R532W mutation and abolished by M518V mutation.
Whole cell voltage clamp recording of macroscopic K+ currents from CHO hm1 cells transfected with GFP and Kv7.2 WT or Kv7.2 containing epileptic encephalopathy mutations. The cells were held at −80 mV. Currents were evoked by depolarization for 1.5 s from −100 mV to +20 mV in 10 mV increments, followed by a step to 0 mV for 300 ms. The raw current traces and data are shown in Supplemental Fig. 3. (A) Representative traces of currents from which leak currents were subtracted at all voltage steps. Leak current was defined as non-voltage-dependent current from GFP-transfected cells. (B-D) Average peak current densities (B), normalized currents (C), and normalized conductance (G / Gmax) (D) were quantified using leak subtracted currents at all voltage steps. The number of transfected cells that were analyzed: GFP (n=9), GFP and Kv7.2 WT (n=11), R333W (n=12), A343D (n=12), M518V (n=8), K526N (n=14), or R532W (n=18). (E) Immunoblotting with anti-Kv7.2 N-terminal antibodies on the lysate from CHO hm1 cells expressing Kv7.2 WT (n=4), R333W (n=12), A343D (n=4), M518V (n=4), K526N (n=4), or R532W (n=4). GAPDH served as a loading control. Data shown represent the Ave ± SEM (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005).