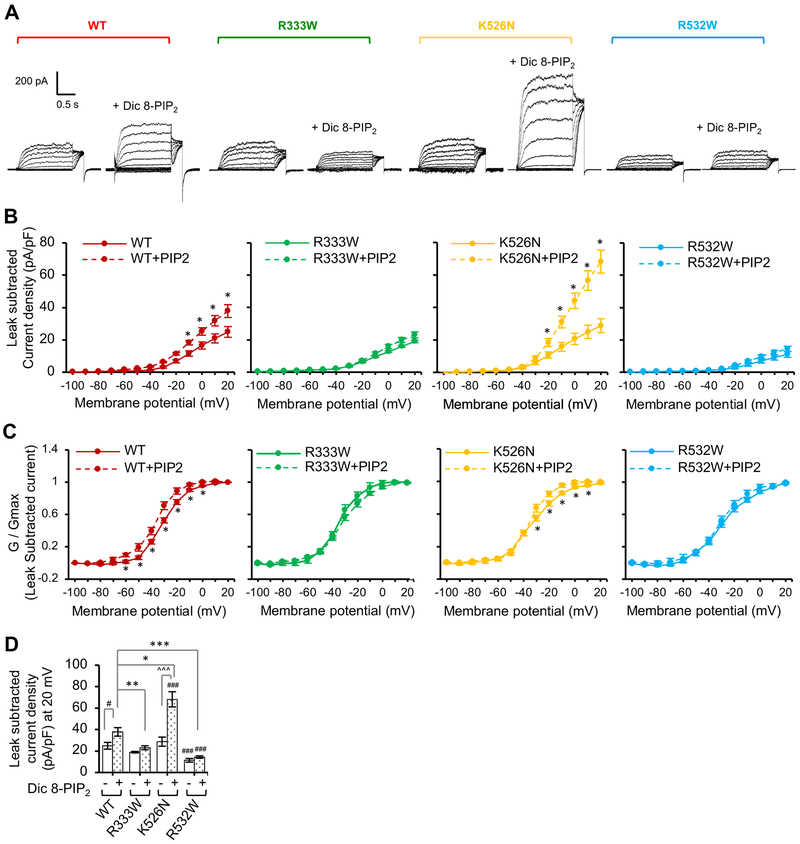
Figure 5. PIP2 stimulation of Kv7.2 current is decreased by R333W and R532W mutations and increased by K526N mutation.
Whole cell patch clamp recording of Kv7.2 currents from CHO hm1 cells with or without diC8-PIP2 (100 μM) in the patch pipette solution using the same voltage clamp protocol as described in Figure 4. The raw current traces and data are shown in Supplemental Fig. S4. (A) Representative leak-subtracted current traces. (B-C) Average peak current densities (B) and normalized conductance (G / Gmax) (C) were quantified using leak subtracted currents at all voltage steps. (D) Average leak subtracted peak current densities at + 20 mV in the absence or presence of diC8-PIP2. The number of GFP-cotransfected cells that were analyzed without diC8-PIP2: Kv7.2 WT (n=11), R333W (n=12), K526N (n=14), or R532W (n=18). The number of GFP-cotransfected cells that were analyzed with diC8-PIP2: Kv7.2 WT (n=8), R333W (n=13), K526N (n=14), or R532W (n=11). Data shown represent the Ave ± SEM (#p<0.05, ###p<0.005 compared to WT without diC8-PIP2, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005 compared to WT with diC8-PIP2, and ^^^p<0.005 compared to K526N without diC8-PIP2)