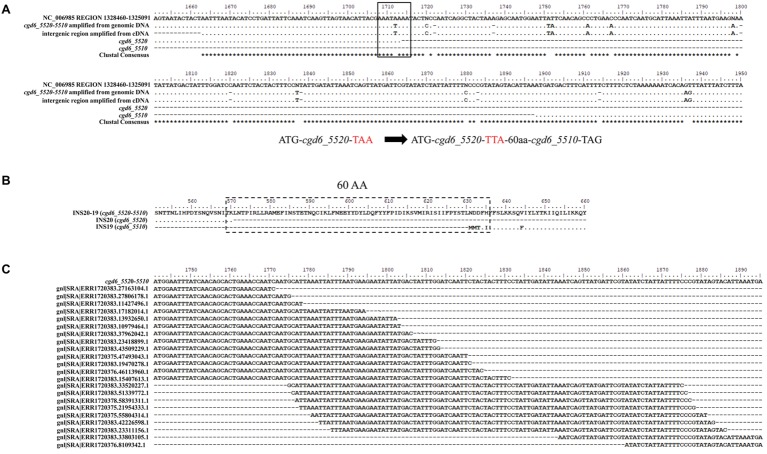
Figure 1.
Evidence for the single gene nature of cgd6_5510 and cgd6_5520. (A) Nucleotide sequence alignment of cgd6_5520-5510 with the references cgd6_5510 (XM_625315.1), cgd6_5520 (XM_001388322.1), and nucleotides 1,325,091-1,328,460 of NC_006985. In the originally predicted intergenic region, there were seven nucleotide substitutions and seven nucleotide insertions, and the substitution of T by A (black box) at position 1,712 of the cgd6_5520 in the reference genome had led to the introduction of a termination codon “TAA.” (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of INS20-19 (encoded by cgd6_5520-5510) with INS20 (encoded by cgd6_5520, XP_001388359.1) and INS19 (encoded by cgd6_5510, XP_625315.1) around the originally predicted intergenic region. In the new annotation, the translation continues until the termination codon of cgd6_5510, and there was an insertion of 60 amino acids (dashed box) between sequences encoded by cgd6_5520 and cgd6_5510. (C) Mapping of C. parvum RNA-Seq reads to the intergenic region of the cgd6_5520-5510 gene. The intergenic regions between cgd6_5520 and cgd6_5510 are nucleotides 1,714–1,891 of cgd6_5520-5510. RNA-Seq reads of ERX1790335 were downloaded from the NCBI SRA database and mapped to the intergenic region between cgd6_5520 and cgd6_5510. The existence of overlapping reads indicates that the originally predicted intergenic region is indeed transcribed. All sequence alignments were manually adjusted for structurally equivalent by introducing gaps. The nucleotides or amino acids identical to the sequence in the reference (the first line of the alignment) are shown as dots in A and B.