Fig. 6:
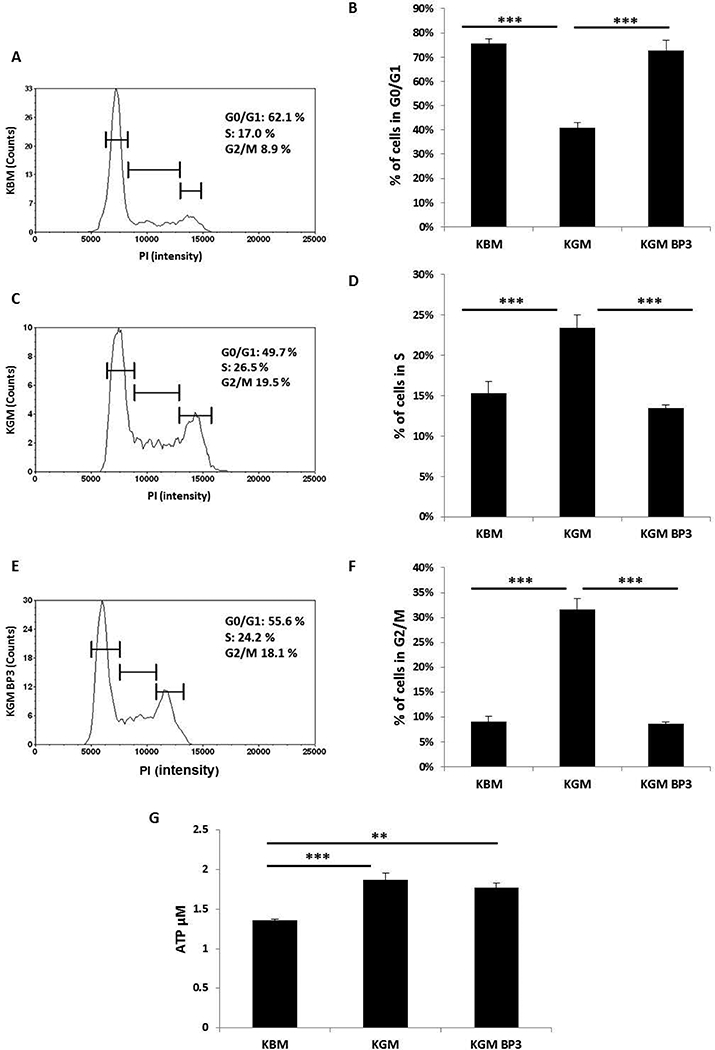
IGFBP-3 induces cell cycle arrest but does not alter cellular respiration. (A, C and E) Representative graphs of cell count as a function of PI intensity in (A) basal media; (C) growth media; (E) growth media supplemented with 100 ng/ml rhIGFBP-3. (B) hTCEpi cells cultured in basal media showed an increase in the proportion of cells in G0/G1 compared to growth conditions (***P<0.001, One-way ANOVA, Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test). Treatment with rhIGFBP-3 also produced a corresponding arrest in the cell cycle (***P<0.001, One-way ANOVA, Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test). (D) hTCEpi cells cultured in growth media showed an increase in the number of cells in S phase compared to cells cultured in basal media and growth media supplemented with rhIGFBP-3 (***P<0.001, One-way ANOVA, Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test). (F) Cells cultured in basal media showed a corresponding decrease in the number of cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle compared to growth media and growth media supplemented with rhIGFBP-3 (***P<0.001, One-way ANOVA, Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test). Data shown as a composite of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. (G) Quantitative determination of ATP levels (μM). hTCEpi cells were cultured in basal or growth media with or without 100 ng/ml rhIGFBP-3 for 24 hours. ATP levels were significantly higher in growth media with or without IGFBP-3 compared to basal media (***P<0.001; **P<0.01, One-way ANOVA, Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test). KGM: keratinocyte growth media; KBM: keratinocyte basal media; BP3: IGFBP-3. Data representative of 5 independent experiments performed in triplicate. All data represented as mean ± standard deviation.
