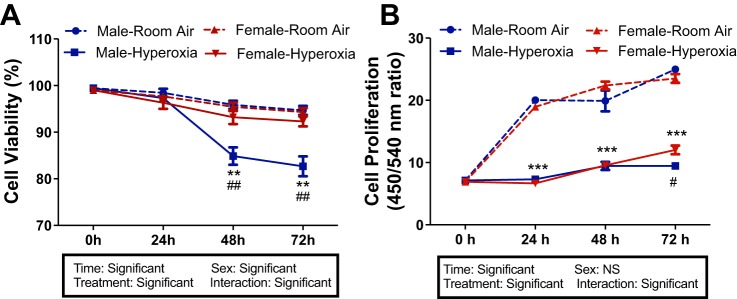
Fig. 3.
Female human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMECs) have preserved cell viability upon exposure to hyperoxia. Male and female HPMECs exposed to room air (RA) (RA-5% CO2) and 24, 48, or 72 h of hyperoxia (95% O2-5% CO2) were subjected to Trypan blue exclusion (A) or a bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assay (B) as described in materials and methods. Values are means ± SE of 3 independent biological replicates (n = 3/group). Significant differences between baseline and subsequent time points within the same sex are indicated by **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; significant differences between male and female HPMECs at each time point are indicated by #P < 0.5 and ##P < 0.01. NS, not significant.